A. A. Somkin, S. A. Konstantinov
“Elective courses in physical education” as a motivational and value component in students’ classes at St. Petersburg State Institute of Culture and Technology
The formation of a sustainable need for constant and systematic physical education and the cultivation of the so-called “fashion for an active and healthy lifestyle” are the most important tasks of such academic disciplines as “Physical Education” and “Elective Courses in Physical Education” in higher educational institutions of the Russian Federation. In accordance with the federal state educational standard of higher education “3 plus” (FSES VO 3+), full-time students at the St. Petersburg State Institute of Film and Television (SPbGIKiT) in the basic part of Block 1 “Disciplines (modules)” of the undergraduate program in physics culture the following academic disciplines are taken:
- “Physical culture” in the amount of 72 academic. hours (16 hours - lectures; 16 hours - practical, seminar classes; 20 hours - independent studies) in the first year;
- “Elective courses in physical education” in the amount of 328 academic. h (practical classes) in the first to third years.
“Elective courses in physical education” involve a gradual transition in St. Petersburg State Institute of Culture and Technology from compulsory forms of training to individual choice of the type of physical education and sports activity by the students themselves. As elective courses at the Department of Physical Education of St. Petersburg State Institute of Culture and Technology, students are offered:
Firstly, standard training sessions in accordance with the schedule (twice a week for two academic hours);
Secondly, various forms of sectional classes that are focused on non-commercial elite sports, physical culture and conditioning sports, applied disciplines, recreational and rehabilitation forms of physical activity, and intellectual sports.
When organizing educational and sectional classes in the discipline “Elective courses in physical education,” the so-called motivational-value component comes to the fore, which should form in young people a positive emotional attitude towards classes and a stable desire to make quite conscious volitional efforts aimed at physical improvement of personality. Let's consider the main forms of sectional classes at the department,
aimed, inter alia, at students who, due to their health status, belong to a preparatory or special medical group.
1. Non-commercial elite sport implies successful performance in high-level competitions, but without receiving significant financial reward. For students of St. Petersburg State Institute of Culture and Technology, specializing in the martial arts Wushu Sanda, these are Russian championships, large and prestigious international tournaments, including in China, the “homeland” of this sport. Wushu Sanda is a combined martial arts form that incorporates the best techniques from Chinese martial arts. With a high level of training of the leading student athletes of the institute in wushu sanda (technical, functional, physical, tactical), they are able, with a certain adaptation of the educational and training process, to represent the institute’s national team in various “related” disciplines - striking, wrestling and mixed martial arts.
2. Physical education and conditioning (or the so-called “mass”) sport is a type of public (ordinary) sport, aimed mainly at physical education and sports training, which contribute to the preservation of previously acquired (at school age) physical shape with strictly regulated participation in competitions . Here, the target outcome of the activity is focused not on the maximum possible result, but on the level of physical and spiritual development necessary for each person to maintain his capacity and adequate state of health. At the same time, the time spent on classes is optimally minimized and does not interfere with the main socially necessary activity of a student receiving higher education. Sectional classes in the following sports are organized on a regular basis at St. Petersburg State Institute of Culture and Technology:
Sports games - volleyball, basketball, table tennis;
Martial arts - kickboxing, taekwondo, sambo, judo;
Athletic sports - arm wrestling and kettlebell lifting;
Cheerleading.
From the best students attending these sections, national teams of the institute are formed, for which the main competition is the Spartakiad of higher educational institutions of St. Petersburg.
3. Applied disciplines. The problem of individual human self-defense in the conditions of a modern metropolis is now becoming extremely relevant. Therefore, it is no coincidence that St. Petersburg State Institute of Culture and Technology is very popular among students (both boys and girls) who do not have the desire to re-
regularly train to participate in competitions, use sections in applied disciplines:
Self-defense - based on the techniques of traditional wushu schools;
KENPO - real hand-to-hand combat;
Aikido, including the use of weapons;
SgobbRI is a system of so-called functional circuit training using exercises from various martial arts (boxing, taekwondo, judo, sports-combat sambo).
Classes in sections such as self-defense and aikido, as a rule, do not require students to develop their physical abilities at a high level or master complex technical techniques.
4. The next group of sections is conditionally united by recreational and rehabilitation forms of physical activity of students. During classes in these sections, physical exercises and some elements of sports are used in accessible and simplified forms to solve the following problems: maintaining and strengthening health; active, healthy rest; switching to another type of activity; restoration of performance; organizing emotionally rich leisure; improving the health of students who, due to their health status, belong to the preparatory and special medical groups.
The fitness section is aimed at students who do not have any deviations in their health. Fitness classes are conducted in the form of so-called “mixed classes” - this means the presence of both aerobic and strength exercises present in the training program. A yoga section is organized for students assigned to the preparatory and special medical groups based on the results of an in-depth medical examination (IME). The first day of the week is a lesson for beginners (mostly first-year students) and those who, due to their health status, belong to a preparatory or special medical group. The second day of the week is a class for students (M-M courses) who have previous experience in yoga, for example in their first year.
5. Sections on intellectual sports - chess and checkers - to which students who have deviations in their health or are exempt from practical classes are oriented to attend. From the best players, based on the results of control training, institute teams are formed in these sports, which regularly participate in regional and city tournaments, as well as in the Spartakiad of higher educational institutions of St. Petersburg.
Thus, the introduction of the new Federal State Educational Standard for Higher Education 3+ in higher educational institutions of the Russian Federation and the allocation in block 1 -
the basic part of “Disciplines (modules)” - the subject “Elective courses in physical education” in St. Petersburg State Institute of Culture and Technology made it possible to move from traditional forms of conducting practical classes in physical education to a personally oriented health program; from compulsory training sessions to individual choice of the type of physical education and sports activity by the students themselves.
Bibliography
1. Kondakov V.L. System mechanisms for designing physical education and health technologies in the educational space of a modern university: monograph. - Belgorod: LitKaraVan, 2013. - 454 p.
2. Matveev L.P. Reflections on sports // Sports management. -2004. - No. 1. - P. 16-21.
3. Matveev L.P. General theory of sports and its applied aspects. - 4th ed., rev. and additional - St. Petersburg: Lan, 2005. - 384 p.
4. Somkin A.A., Makarov O.R. Development of mixed martial arts “Wushu Sanda” in a non-specialized higher educational institution // Current state and prospects for the development of psychology and pedagogy: collection. articles of the International scientific and practical. conf. (February 28, 2015, Ufa). - Ufa: Aeterna, 2015. - pp. 165-170.
V. G. Sotnik
Modernization of teacher education in the Russian Federation
In the 21st century, the Russian education system is undergoing dramatic changes.
A number of regulatory documents have been adopted in the Russian Federation (a new law on education, federal state educational standards), and therefore there is a need to move from a knowledge-based educational paradigm to a competency-based one. Consequently, students are required to have significant independence in carrying out active cognitive activity.
What education will be like in the 21st century depends on the teacher, his life position, professionalism, and competence. Research competence in education is considered as the main component of the professional competence of a biology teacher.
The competency-based approach is considered by some authors as a unique response to the problematic situation in education that has arisen as a result of the contradiction between the need to ensure modern quality of education and the impossibility
Basic step – basic step
Step-touch - additional step
Double Step-touch - two additional steps
Step-tap - step touch
Step-lift – step swing
Step- front – swing forward
Step-back - swing back
Step-side - swing to the side
Step-curl - step overlap
Step-kick - step kick
Step-plie - step squat
Scoop - side step
Grape wine – cross step
Knee lift or Knee up - knee lift
Kick - leg swing
Low kick - kick with the shin
Jumping jack - jump
Twist jump – jump on two legs
Pendulum - changing the position of the legs using jumps
Lunge - lunge
March - march
Marching - walking in one place
Walking – walking in different directions
Mambo – step with alternating “extension” of legs in the forward-backward direction
Rock step - step with alternating “extension” of legs in a diagonal direction
V-step – movement of the legs, which are associated with the letter “V”
Straddle - walking in which you step with your right foot to the right
Cross – cross step
Cha-cha-cha - a triple step that is part of a dance movement
Polka – a simple variation of the polka dance move
V-mambo – a combination of two steps V-step and Mamb
You can do athletic gymnastics all answers are correct.
Athletic gymnastics goes well together all answers are correct.
Tennis grew out of badminton.
More than 100 years ago, an enterprising ..... registered the invented name “Ping Pong” John Jaques.
In Ancient Greece they used exercises with galters - the prototype dumbbells.
Used as weights in athletic gymnastics all answers are correct.
The most important specific indicators of a physically perfect person of our time are all answers are correct.
A sport formed on the foundation of recreational aerobics, which combines dance movements to high-tempo musical accompaniment and strength elements of varying complexity sports aerobics.
The volleyball court is conventionally divided into 6 zones.
Men's volleyball net height 243 cm.
Women's volleyball net height 224 cm.
Used instead of a ball to play volleyball rubber chamber.
Task ((1))TK1. Sun hardening Vitamin D is produced in the skin.
Task ((1))TK1. After university classes and lunch... you need to spend some time relaxing 1.5-2 hours.
Task ((1))TK1. The following subjective factors influence the formation of motives that encourage students to engage in independent studies and active physical education and sports: all answers are correct.
Task ((1))TK1. Systematic use of water procedures a reliable preventative against the harmful effects of various accidental cooling of the body.
The table tennis player who must hit the ball first in a rally "Server".
Yoganestics program of classes using roller skates indoors on a special surface.
Each play of the ball in table tennis is tempered by appropriation one point to one or another player (team).
Number of players in a volleyball team 6 .
Number of reserves in table tennis unlimited.
The football team consists of of 11 players.
The International Volleyball Federation was founded in 1947.
IOC – International Olympic Committee.
A ball scored by a football player against his team own goal.
Table tennis ball orange.
Reliable support for the human body skeleton.
The title of the latest publication in our country of K. Cooper's book Aerobics for good health.
Building muscle mass in athletic gymnastics of all parts of the body with a health focus wellness stage.
Cheating movements in football are performed in direct combat with an opponent feints.
One of the most popular and massive collective sports games football.
One of the oldest sports games in the world badminton.
The optimal height of the step platform, which is used in a recreational aerobics class 10-15 cm.
Mastering the game of volleyball begins from studying stances and movements.
Main time of football game 2 halves of 45 minutes.
The main attacking and defensive action in the game of table tennis hit.
Points in table tennis are awarded to a player in the following cases: all answers are correct.
The period of time in table tennis when the ball is in play "Raffle".
According to modern international rules established in 2001, each table tennis game lasts until 11 points.
When playing the ball in volleyball, it is allowed to perform 3 touches.
The size of the volleyball court is 9x18 m.
The birthplace of athleticism Ancient Greece.
A draw, the result of which is counted in table tennis "Point".
Free guard in volleyball "libero".
A system of physical exercises using special weights athletic gymnastics.
Soviet football players became Olympic champions 1956 and 1988.
Modern health aerobics is associated with the name Cooper's Canneta.
A person’s ability to most rationally master new motor actions and successfully solve in changing conditions dexterity.
Step aerobics is exercises performed on a special platform.
This is what a football commentator usually says about the team in whose stadium the match is taking place. home team.
Flexibility exercises are stretching.
Physical activity with weights makes muscles stronger, joints more mobile, the body more resilient.
Footballer who was recognized as the best goalkeeper in the world in 1988 Rinat Dasaev.
Net playing time in football is 55-60 min.
A stage in athletic gymnastics aimed at achieving a certain level of strength qualities developmental stage.
A stage in athletic gymnastics aimed at creating the desired physique relief and figure correction formative stage.
This is taken into account when a football player is named top scorer goals scored.
Sections: Sports at school and children's health
The program of the elective course in physical education “General Physical Education” was developed for students of 9th grade of the profile level, taking into account the physical development of students, the capabilities of the sports base and based on the requirements for students completing basic general education and is designed for 34 hours or 1 hour per week.
Goal: increasing the physical activity of students, forming the foundations of a healthy lifestyle, and general improvement of the body.
- teach the student ways to creatively apply acquired knowledge, skills and abilities to maintain a high level of physical and mental performance, health status, and improve developed competencies;
- improvement of specific motor actions, development of motor abilities, formation of skills to independently train and carry out physical education and sports activities; ?
- give the student the opportunity to realize his interest in the subject;
- to clarify the student’s readiness and ability to master the chosen subject at an advanced level;
- create conditions for preparing for an elective exam in the subject “Physical Education”;
- to enable students to use the acquired knowledge in their future life and practical activities.
The methodological basis of this elective course program is the Educational Standards of Basic General Education in Physical Education (basic and specialized level).
The system of arrangement of the material, the completeness of the presentation of information, the nature of the selection of material are aimed at achieving the educational, educational, information goals outlined in the State Standard: promoting health, promoting harmonious development, acquiring the necessary knowledge in the field of physical culture and sports, promoting the development of moral and volitional qualities, development of mental processes and personality traits.
The material and technical base of the school allows the following sports to be included in the designated course: athletics, volleyball, basketball, table tennis, gymnastics with elements of acrobatics, shaping.
This work program is a type 2 program, since the number of hours allocated for mastering the educational material differs significantly from that in the program of the authors V.I. Lyakh and A.A. Zdanevich. In addition, in the proposed program, the educational material is supplemented with such sections as “Table Tennis” and “Shaping”, and the material in the section “Fundamentals of knowledge about physical culture” is studied in the context of a specific sport and is of leading importance in the applied nature of this elective course.
1. Basic knowledge
- features of the development of the chosen sport;
- pedagogical, physiological and psychological foundations of teaching motor actions and developing physical qualities, modern forms of constructing classes and systems of physical exercises with different functional orientations;
- biodynamic features and content of physical exercises of a general developmental and corrective nature, the basis of their use in solving problems of physical development and health promotion;
- age-related features of the development of leading mental processes and physical qualities, the possibility of forming individual traits and personality traits through regular physical education classes;
- psychofunctional characteristics of one’s own body;
- individual ways to control the development of adaptive properties of the body, improve health and increase physical fitness;
- methods of organizing independent physical exercises with different functional orientations, rules for using sports equipment and equipment, principles for creating the simplest sports facilities and playgrounds;
- rules of personal hygiene, injury prevention and first aid during physical exercise.
2. Athletics
- Running at a steady pace: 20–25 min. (boys), 15–20 min. (girls);
- Variable pace running: 10–15 min.
3. Sports games:
Volleyball
- player stance and movement;
- passing the ball;
- bottom feed;
- receiving the ball after serving;
- two-way game;
- direct attack strike;
- single blocking.
Basketball
- stances, movements, stops, passes and catching the ball;
- dribbling the ball with the right and left hand;
- throwing the ball with one or two from a place and in motion.
4. Gymnastics with elements of acrobatics
- vault with legs bent;
- acrobatics: back rolls; stand on the shoulder blades, turns to the side; two somersaults forward; bending upward jump.
5. Table tennis
- movement;
- hits and serves left and right;
- straight blows with rotation;
- Single player game.
6. Shaping
- general impact exercises;
- exercises for abdominal muscles;
- exercises for back muscles;
- exercises for the gluteal muscles;
- exercises for the hip abductors;
- hip extensor muscles;
- exercises for the muscles of the upper shoulder girdle;
- development of various muscle groups with changes in dosage in time, quantity and intensity of exercises.
Requirements to prepare students:
Upon completion of studying the general physical training course program, students must demonstrate the following: knowledge :
Features of individual physical education and sports classes;
Basic concepts of a healthy lifestyle;
Basics of sports hygiene;
Dosage of individual physical education and sports classes.
Motor skills and abilities:
Technically correctly perform basic movements in the proposed sports;
Demonstrate the implementation of an individually developed set of general physical training exercises.
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND SCIENCE OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION Birsk branch of the federal state educational budgetary institution of higher professional education "Bashkir State University"
Faculty of Social Sciences and Humanities Department of History, Philosophy and Social Sciences and Humanities
Work program of the discipline “Elective courses in physical education”
Direction of training
03/44/05 TEACHER EDUCATION
Training profile History\Law
Graduate qualification (degree) Bachelor
Form of study – Full-time/correspondence
AGREED
I. ORGANIZATIONAL AND METHODOLOGICAL SECTION ……………………………………....…6
Purpose of the courses…….………………………………………………………………………………..…..6 Learning objectives of the courses……… …………………………………………………………...…..….6 The place of the discipline in the structure of the OPEP HE (the main professional educational program of higher education)…………… ……………………………………………………..6 Requirements for the results of mastering the content of the discipline…………………………….……7 Forms of control……… …………………………………………………………………………………….…....7
III. EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY …………………………………………………….18
IV EDUCATIONAL AND METHODOLOGICAL, INFORMATIONAL AND MATERIAL AND TECHNICAL SUPPORT OF DISCIPLINE ……………………………………..…..18 Recommended reading…………………………………………………………………………………. ….18
Recommended training, reference and information, monitoring and other computer programs used in the study of the discipline…………………………..19 Logistics support for the discipline (sections)……………………………. .…...19 V ASSESSMENT TOOLS……………………………………………………………….....19 sample topics for essays9 Questions for
test………………………………………………………………………………….....20
VI. THEMATIC PLAN FOR STUDYING A DISCIPLINE …………………………….....22 Applications……………………………………………………………………………………………… …………….....3 1 Appendix
1………………………………………………………………………………......35 Appendix 2………………… …………………………………………………………………………………... …...38
I ORGANIZATIONAL AND METHODOLOGICAL SECTION 1.1 The purpose of elective courses in physical education:
The purpose of elective courses in physical education is the formation of general cultural competencies: OK-8 the ability to use methods and means of physical education to ensure full-fledged social and professional activities;
1.2 Educational objectives of elective courses in physical education:
The objectives of the courses are:
1. maintaining and strengthening the health of students, promoting the proper formation and comprehensive development of the body, maintaining high performance throughout the entire period of study;
2. understanding the social significance of applied physical culture and its role in personal development and preparation for professional activity;
3. knowledge of scientific, biological, pedagogical and practical foundations of physical culture and a healthy lifestyle;
4. formation of a motivational and value-based attitude towards physical culture, an attitude towards a healthy lifestyle, physical improvement and self-education of the habit of regular exercise and sports;
5. mastering a system of practical skills that ensure the preservation and strengthening of health, mental well-being, development and improvement of psychophysical abilities, qualities and personality traits, self-determination in physical culture and sports;
6. acquiring personal experience in improving motor and functional capabilities, providing general and professional-applied physical preparedness for future profession and life;
7. acquisition by students of the necessary knowledge on the basics of theory, methodology and organization of physical education and sports training, preparation for work as public instructors, coaches and judges;
8. creating a basis for creative and methodologically sound use physical education and sports activities for the purpose of subsequent life and professional achievements;
9. improving the sports skills of student athletes.
1.3 Place of courses in the structure of the OPOP HE elective courses in physical education belong to the basic part of the curriculum and constitute an independent section.
To successfully complete the courses, the student must:
1. the importance of physical culture in the formation of a general culture of the individual, introduction to universal values and a healthy lifestyle, strengthening human health, preventing bad habits, maintaining a healthy lifestyle through physical culture in the process physical education and sports activities;
2. scientific foundations of biology, physiology, theory and methodology of pedagogy and practice of physical culture and healthy lifestyle;
3. content and orientation of various systems of physical exercises, their health-improving and developmental effectiveness.
1. take into account the individual characteristics of the physical, gender, age and mental development of those involved and apply them during regular physical exercise;
2. conduct independent physical exercises with general developmental, professional-applied and health-corrective orientation; 3. create individual sets of physical exercises with different directions.
1. a set of exercises aimed at improving health, teaching motor actions and developing physical qualities;
2. ways to determine the dosage of physical activity and the direction of physical exercise;
3. insurance techniques and methods of providing first aid during physical exercise.
1.4. Requirements for the results of mastering the course content
As a result of mastering the courses, the following competencies should be formed: OK-8 the ability to use methods and means of physical culture to ensure full-fledged social and professional activity; As a result of mastering the OK-8 competency, the student must: acquire
the ability to use methods and means of physical culture to ensure full-fledged social and professional activities;
1.5 Forms of control
Current and boundary control carried out by a teacher conducting practical classes in accordance with the thematic plan.
Current and milestone certification in semesters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 – pass

The results of ongoing monitoring and intermediate certification form the rating assessment of the student’s work. The distribution of points when forming a rating assessment of a student’s work is carried out in accordance with the “Regulations on the rating system for assessing the progress and quality of knowledge of students in the federal state budgetary educational institution of higher professional education” Russian University of Economics named after G.V. Plekhanov." The distribution of points for certain types of work in the process of mastering the discipline “Applied Physical Culture” is carried out in accordance with Appendix 1.
Scope of discipline and types of academic work
Correspondence course Type of work
Total labor intensity Classroom work:
Lectures (L) Practical exercises (PL) Laboratory work (LB) CSR
Independent work:
Self-preparation (study and repetition of lecture material and material from textbooks and teaching aids, preparation for practical classes, colloquiums, midterm tests, etc.)
Preparation and passing the test
Type of final control: test
Labor intensity, hours
1 semester |
|

II. COURSE CONTENTS |
|||||||||||||||||
Name |
|||||||||||||||||
Molded |
|||||||||||||||||
courses section |
Results of mastery (know, be able, own) |
||||||||||||||||
competencies |
|||||||||||||||||
Physical culture and sport as social |
Know: |
professional |
|||||||||||||||
Physical |
phenomena of society. Current state |
solidarity and corporatism, understanding |
|||||||||||||||
culture in |
physical culture and sports. Federal Law No. 329 “On |
duty and honor |
|||||||||||||||
general culture |
physical culture and sports in Russian |
Be able to: decide |
|||||||||||||||
Federation". Physical culture of the individual. |
production |
||||||||||||||||
professional |
The essence of physical culture as |
on a professional level, find contact |
|||||||||||||||
social institution. Values |
with all team members |
||||||||||||||||
preparation |
physical culture. Physical Culture |
Possess: knowledge of professional ethics |
|||||||||||||||
students. |
as an academic discipline of higher education |
||||||||||||||||
vocational education and |
allowing |
||||||||||||||||
holistic personality development. Values |
organizational and managerial work in |
||||||||||||||||
orientations and attitudes of students towards |
team at a high modern level |
||||||||||||||||
physical culture and sports. Basic |
|||||||||||||||||
provisions of the organization of physical |
|||||||||||||||||
education in a higher educational institution. |
Know: |
||||||||||||||||
Topic 2. Social |
Organism |
person |
Basic |
||||||||||||||
biological |
self-developing |
self-regulating |
physical education, the role and place of physical |
||||||||||||||
basics of physical |
biological |
Impact |
culture and sports in ensuring health |
||||||||||||||
culture. |
natural |
socio-ecological |
nation and promoting socio-cultural |
||||||||||||||
factors on the body and vital functions |
development of society, methods and means |
||||||||||||||||
person. Means of physical culture and |
physical |
culture |
provision |
||||||||||||||
sports management |
improvement |
social |
professional |
||||||||||||||
functional capabilities of the body in |
activities, |
independent, |
|||||||||||||||
to ensure mental and physical |
correct |
use |
|||||||||||||||
activities. Physiological mechanisms and |
physical education and health promotion |
||||||||||||||||
patterns |
improvement |
Be able to: Find effective methods and |
|||||||||||||||
individual |
body |
facilities |
physical |
culture |
|||||||||||||
influence |
directed |
physical |
ensuring social and professional |
||||||||||||||
workout. |
Motor |
activities, |
identify positive |
||||||||||||||
increasing the resistance of the human body |
negative |
physical |
|||||||||||||||
Educational
technologies
Practical
Independent
students.
Discussion
abstracts.
Consultations
teachers.
Practical
Independent work of students Discussion of abstracts. Teacher consultations.

to different environmental conditions |
preparation, |
Right |
use |
||||||
physical education methods both in theory and |
|||||||||
on practice |
|||||||||
By means |
independent |
||||||||
methodically |
correct |
use |
|||||||
physical education |
and strengthening |
||||||||
health, |
readiness |
achieving |
|||||||
due |
physical |
||||||||
preparedness |
provision |
||||||||
full social and professional |
|||||||||
Topic 3.Basics |
Human health as a value and factors |
Know: the relationship between a student’s general culture |
|||||||
healthy image |
its defining ones. General relationship |
and his way of life. |
Practical |
||||||
life. Physical |
student's culture and lifestyle. |
Be able to: use knowledge of a healthy lifestyle |
|||||||
culture in |
Healthy lifestyle and its components. |
in professional and social life |
Independent |
||||||
ensuring |
Personal attitude to health as a condition |
Possess: personal and social skills |
student work |
||||||
health. |
formation of a healthy lifestyle. |
hygiene and age physiology |
Discussion |
||||||
Criteria for the effectiveness of a healthy image |
abstracts |
||||||||
2.2. Providing course content
Topic 1. Physical culture in general cultural and professional training of students.
Literature: O-1; O-2;O-3; N-1, N-2, D-1; D-9 Questions for self-test:
1. Expand the concept of physical culture.
2. Name the functions of physical culture.
3. What is physical perfection?
4. What are the indicators of physical perfection?
5. Expand the concept of physical education.
6. What principles is the domestic system of physical education based on?
7. What is physical training.
8. Name the types of physical training.
9. What is physical development?
1. Take measurements of your height, weight and mass, calculate the indices of their ratios.
2. Enter data into your diary once a month and determine the dynamics of indicators throughout the year.
Topic 2. Socio-biological foundations of physical culture.
Literature: O-1;O-2;O-5;D-1; D-9, D-13 Questions for self-test:
1. What types of bones does the human body consist of?
2. Define the concept of joint and name the types of joints.
3. Name the main types of muscles and their functions.
4. Define the concept of sarcomere and determine its functions.
5. Which muscle fibers have faster contractility?
6. What is glycogen broken down into during anaerobic processes of energy production?
7. What is formed during the oxidation of carbohydrates and fats?
8. Which process of energy formation is most effective during long-term physical work.
9. Define cardiovascular system and characterize changes in its functioning during physical activity.
10. Define the respiratory system and characterize changes in its functioning during physical activity.
Tasks for independent work:
1. Determine heart rate and blood pressure at rest and during exercise.
2. By performing loads of varying intensity and measuring heart rate and blood pressure, determine how they depend on the magnitude of the load.
Topic 3. Basics of a healthy lifestyle. Physical culture in ensuring health.
Literature: O-1; O-2, O-3; N-1;D-9; D-4, D-12, D13 Questions for self-test:
1.What does a healthy lifestyle involve?
2. What is human health (as defined by the World Health Organization)?
3. Name the groups of risk factors that affect human health.
4. Name the integral indicator of a person’s physical health.
5. What is MPC (DMPC). How does human health depend on this value?
6. Name the main indicators of homeostasis in a healthy person (pressure, heart rate, plasma pH, respiratory rate, glucose concentration).
7. Give the formula for effective nutrition and the proportions of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in food.
8. Name the main functions of nutrition.
9. What should be the power of the training load (in % of the maximum level of physical performance) in health training?
10. Name the most effective method of health training.
Tasks for independent work:
1. Calculate your daily energy consumption.
2. Balance your intake of major energy sources with your daily consumption.
Topic 4. Psychological foundations of educational work and intellectual activity. Means of physical culture in regulating performance.
Literature: O-1;O-2;O-5;D-9; D-4; D-11. Self-test questions:
1. After what period of time after the start of school during the school day do students exhibit optimal (sustained) mental performance?
2. What is the typical dynamics of students’ mental performance during the school week?
3. Does the change in the physical performance of students during the school week correspond to the dynamics of their mental performance?
4. During what periods during the academic year do students experience the greatest decline in mental and physical performance?
5. Is it possible to effectively solve the problems of improving the health and increasing the performance of students during their studies at a university only within the framework of physical education classes?
6. What “small forms” of physical exercises exist in the academic work regime of students?
Tasks for independent work:
1. Study the dynamics of your own performance throughout the day.
2. Balance your work-rest ratio for the most efficient performance.
Topic 5. General physical and special training in the physical education system
Literature: O-1;O-2;D-1; D-6; D-10. Self-test questions:
1. What is physical training?
2. What is the essence of general physical training?
3. What does special physical training include?
Topic 6. Fundamentals of methods of independent physical exercise.
Literature: O-1; O-2;O-4;D-5; D-8; D-12 Questions for self-test:
1. What forms of independent study exist.
2. How the nature of the content of classes changes depending on age.
3. What is the motivation and purposefulness of independent studies. 4.Features of independent studies for women.
5. Limits of load intensity in conditions of independent training for people of different ages.
6. Self-monitoring of the effectiveness of independent studies.
Tasks for independent work:
1. Create a morning exercise routine from 12-15 exercises.
2. Perform the complex daily and notice an increase in the overall performance of the body.
Topic 7. Sports. Individual choice of sports or physical exercise systems.
Literature: O-1;O-2;N-1; N-2;D-6; D-8. Self-test questions:
1. Define the concept of sport.
2. What are the distinctive features of competitive activity?
3. What changes in a person’s functional state does a competitive environment cause?
4. What is mass sport (sport for everyone)?
5. What is elite sport (Olympic sport)?
6. What is professional (entertainment and commercial) sport?
Topic 8. Features of practicing a chosen sport or system of physical exercises.
Literature: O-1;O-2;D-6; D-8; D-12; D-13 Questions for self-test:
1. Give a physiological explanation for the concept of supercompensation phase (super-restoration of energy sources, excitability of the nervous system)?
2. Which method of physical education involves precise dosage of load and rest?
3. What methodological principle of physical education involves a gradual and constant increase in requirements for students?
4. How does the competitive environment affect the physiological effect of physical exercise?
Tasks for independent work:
1. Choose a distance that you can easily cover while running at the lowest work intensity.
2. Run this distance every other day at the same time for 1–2 months regularly and find out how much easier your body copes with the load (systematicity will lead to super-recovery of the body).
Topic 9. Diagnostics and self-diagnosis during exercise and sports
Literature: O-1;O-2;N-1;D-2; D-9, D-13. Self-test questions:
1. What is the frequency of medical monitoring for athletes?
2. Indicate the main purpose of the medical examination.
3. What determines the physical development of a person?
4. What type of posture is considered normal?
5. What characteristics underlie anthropometric standards?
6. What is the correlation method based on?
Tasks for independent work:
1. Take measurements of heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate at rest.
2. Take measurements of the subcutaneous fat layer.
Topic 10. Sports. Choice of sports, features of practicing the chosen sport.
Literature: O-1;O-2; O-3;D-6; D-8; D-12; D-13 Questions for self-test:
1. Describe the characteristics of the impact of sports (systems of physical exercises) on physical development and preparedness, mental qualities and personality traits.
2. Give characteristics of sports that develop individual physical qualities.
3. What are the goals and objectives of sports training in a university setting.
4. Tell us about planning a workout in your chosen sport.
5. What are the main ways to achieve physical, technical, tactical and mental preparedness.
6. Determine the main methods for monitoring the effectiveness of training sessions.
Tasks for independent work:
1. See the tasks of topic 9.
Topic 11. Self-control during physical exercise.
Literature: O-1;O-2; N-1;D-3; D 7; D-13. Self-test questions:
1. What is the purpose of self-control?
2. Specify subjective self-control data
3. Specify objective self-monitoring data
4. What is the breath hold during inhalation (Stange test) in healthy adults?
5. What is the breath hold during exhalation (Genchi test) of trained people?
6. What heart rate should not be exceeded when doing physical exercise at the age of 18?
Tasks for independent work:
1. Conduct a Genci test yourself.
2. Perform the Stange test yourself.
Topic 12. Professional applied physical training (PPPP) of students.
Literature: O-1;N-1;D-1; D-3. Self-test questions:
1. What is professional applied physical training (PPPT)?
2. What is the purpose of PPFP?
3. What are the tasks of the PPFP?
4. What groups can professions be divided into?
5. What basic physiological indicators must be taken into account when assessing the severity of work?
Tasks for independent work:
1. Create a set of physical exercises for your work activity.
Topic 13. Physical culture in the professional activity of a bachelor
Literature: O-1;O-2; N-1D-1; D-2 Questions for self-test:
1. What effect does forced restriction of motor activity during mental activity have on students’ bodies?
2.Do biological rhythms influence human performance?
3. Does the level of physical activity of students during their studies at a university affect their health?
4. What is meant by human motor activity (MA)?
5. What components can human motor activity be divided into?
7. Is it possible to develop certain mental qualities and personality traits with the help of physical exercise (participation in one sport or another)?
Topic 14. The relationship between a student’s general culture and his lifestyle.
Literature: O-1;O-2; O-3; N-1; N-2;D-1; D-2 Questions for self-test:
1. Human health as a value and the factors that determine it?
2. The relationship between a student’s general culture and his lifestyle?
3. A healthy lifestyle and its components?
Topic 15. Criteria for the effectiveness of a healthy lifestyle.
Literature: O-1;O-2; O-3;D-3; D 7; D-13. Self-test questions:
1. Personal attitude to health as a condition for the formation of a healthy lifestyle? 2. Criteria for the effectiveness of a healthy lifestyle?
Topic 16. Possibility and conditions for correction of physical development, physique, motor and functional readiness by means of physical culture and sports at student age.
Literature: O-1;N-2;D-3; D-3. Self-test questions:
1. Correction of physical development.
2. The influence of physical exercise, sports and healthy lifestyle on the functioning of the body and physique growth. 3. Correction of motor and functional readiness.
ABOUT THE INTRODUCTION OF THE AII-RUSSIA PHYSICAL CULTURE
AND SPORTS COMPLEX TRP
N.N. Kalmykov, A.V. Yudkin, A. G. Nosov
Various alternative options of the TRP system development in the Russian Federation, its features, goals, tasks and main functions are considered on the basis of the analysis of the legislative base of the WUSC TRP, normative and legal acts of federal and regional significance. The main proposals and recommendations for improving the organization and quality of implementing this system in educational institutions are formulated. A statistical observation of the organization and implementation of the TRP has been carried out. The main problems connected with informing the population about this complex are revealed.
Key words: sport, health, GTO, legislative framework of the GTO, statistical observation, GTO standards.
Kalmykov Nikolai Nikolaevich, candidate of sociological sciences, director, [email protected], Russia, Moscow, Expert-Analytical Center of the Russian Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration,
Yudkin Artem Vladimirovich, advisor to the chairman of the board, [email protected], Russia, Novosibirsk, Siberian Expert Center "Modernization",
Nosov Alexander Georgievich, candidate of pedagogical sciences, teacher, [email protected], Russia, Saratov, Povolzhsky Institute of Management named after Stolypin of the Russian Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration
UDC 796.011.1:378.14
FORMATION OF STUDENTS' COMPETENCIES WITHIN
ELECTIVE COURSE IN PHYSICAL EDUCATION
L.T. Kudashova, N.N. Vengerova
Problems have been identified in the content of the elective course in physical education with the aim of developing general cultural competencies among students. A methodology for organizing classes in an elective course in physical education at a university using physical education and health technologies is presented, which takes into account the level of physical fitness and emotional state of students and contributes to the formation of specially targeted competencies among female students.
Key words: competencies, elective course in physical education, physical education and health technologies, physical development, physical preparedness.
The modernization of higher education, in particular the introduction of specialized training, opens up fundamentally new opportunities in the implementation of innovative activities at the university. In the context of specialized training, new components are introduced in addition to the basic ones
training - elective courses. Elective courses are the latest mechanism for updating and individualizing the learning process. With a well-developed system of elective courses, each student can receive an education with a certain desired focus in a particular area of knowledge. It is elective disciplines that are essentially the most important means of constructing individual educational programs, because are most closely related to each student’s choice of educational content depending on his interests, abilities, and subsequent life plans. Elective courses most contribute to solving individual problems in the formation of competencies of the educational standard.
When talking about the quality of specialist training at a university, one should take into account not only the acquired knowledge, skills and experience in the professional field, but also psychophysical suitability. There is no doubt that our country's labor reserves must not only be highly qualified, but also have good health. In this regard, as an indisputable provision, each educational standard specifies general cultural competencies aimed at developing readiness to use the means of physical education to increase one’s physical improvement while ensuring full-fledged social and professional activities.
In the Federal State Educational Standard for Higher Education in various areas of training bachelors and specialists, general cultural competencies aimed at physical improvement are formulated in different ways: the student must have “the ability to maintain the proper level of physical fitness to ensure full-fledged social and professional activity, promotion of active longevity, healthy lifestyle and prevention diseases"; “the ability to use methods and means of physical culture to ensure full-fledged social and professional activity”; “readiness to maintain the proper level of physical fitness to ensure full-fledged social and professional activities”; “the ability to apply methods and means of cognition, training and self-control for intellectual development, increasing cultural level, professional competence, maintaining one’s health, moral and physical self-improvement”; “possession of the means of independent, methodically correct use of methods of physical education and health promotion, readiness to achieve the proper level of physical fitness to ensure full-fledged social and professional activity”; “readiness to maintain a level of physical fitness that ensures full-fledged activity”; “the ability to apply methods and means of cognition, learning and self-control for one’s own
intellectual development, raising the cultural level, professional competence, maintaining one’s health, moral and physical self-improvement,” etc., but their essence remains the same.
Physical perfection, according to N.V. Reshetnikov, this is a historically determined level of health and comprehensive development of people’s physical abilities, corresponding to the requirements of human activity in various spheres of social labor, ensuring high human performance for many years. In this context, physical perfection reflects such a degree of physical development of youth, students, their level of health, which allows them to most fully realize their creative potential. Therefore, physical perfection is not just a desirable quality of a future specialist, but a necessary element of his personal structure.
It is physical culture that plays the leading role in solving issues of developing the physical abilities of students. The result of education upon completion of training in the field of physical culture should be the creation of sustainable motivation and need for a healthy and productive lifestyle, physical self-improvement, the acquisition of personal experience in the creative use of its means and methods, and the achievement of an established level of physical fitness.
Currently, the requirements of federal standards for the learning process provide for the discipline “Physical Education” to allocate hours in the basic part (72 hours) and elective courses with mandatory academic hours (328 hours), but without specifying the means and methods of their implementation.
This poses a problem for sports pedagogy science that requires theoretical justification and practical solutions. The ways of implementation lie in the search for effective, attractive and accessible means for students, as well as in improving the physical education process itself. After all, it is elective courses that “compensate” for the largely limited capabilities of basic disciplines in meeting the diverse educational needs of students and shaping their individual educational trajectory.
For physical education teachers at a university, there is an opportunity to make scientifically based changes and additions to elective courses in the forms of organization, content of educational material, summing up the results of its development, taking into account regional, sociocultural, material and technical conditions, the characteristics of students’ professional training, the availability and qualifications of teaching staff. frames.
Not only traditional means of physical culture can be used: exercises in athletics, wrestling, sports games, skiing, swimming, but also the latest modern physical culture and health technologies.
At the moment, in the practice of physical culture, a significant number of different physical culture and health systems have been formed, designed to promote the preservation and strengthening of the health of the population, including students. When using this variety of systems, it is necessary to take into account the value orientations of modern youth so that the orientation towards physical education and sports activities does not weaken.
In addition, the means of physical education used must take into account the gender and age characteristics of students and be aimed at developing in them, during the learning process, certain professionally significant physiological, physical and psychological functions and qualities, health status and their compliance with the nature of the professional requirements of the chosen profession for the formation of appropriate competencies.
At student age, the physical maturation of the body is completed. This period can be called the final stage of the progressive age-related development of the psychophysiological and motor capabilities of the body. Young people during this period have great opportunities for intense educational work and social and political activity. In this age range, the body maintains a relatively high performance capacity and an overall high level of functional activity. At the same time, numerous studies indicate a low level of physical fitness and health among the majority of school graduates. In addition, many lack basic movement culture and the ability to demonstrate vital motor qualities and skills in everyday life. Often, it is with this level of preparedness in physical education that yesterday’s schoolchildren become today’s students, not to mention the fact that all health deviations that appeared in childhood often worsen over the years.
Taking into account all of the above, we conducted research as part of teaching the discipline “Physical Education (elective discipline)”. Female first-year students of St. Petersburg State Economic University took part in our experiment.
A preliminary survey of female students showed that the leading positive motives for attending physical education classes for them are: the desire to improve their figure - 87%, the desire to maintain health - 10%, the need to get a test - 3%. 60.1% of respondents wished to regularly attend physical education classes, in
at the same time, 39.9% of first-year girls indicate a lack of interest in physical education.
The choice of the majority of female students involves the use of modern fitness technologies in physical education classes: preference is given to fitness - 41.2%, callanetics - 40.5%, aerobics - 32.4%; aqua aerobics - 25%.
When forming motor programs within the framework of elective courses in physical education, we used modern physical education and health technologies, taking into account that female students prefer exercises related to music, plasticity, and artistry. The use of dance exercises in health training plays a big role in preventing and relieving stress, psychocomplexes, and general mental health, which is so necessary during intense mental work of students. The variety of exercises, constant updating of logically structured programs, and the high emotional background of classes make it possible to effectively solve most of the problems of physical education in the formation of relevant general cultural competencies.
In our research, as part of an elective course in physical education, first-year students of St. Petersburg State University of Economics studied using means of physical education and health technologies: in the control group (CG), basic aerobics exercises were mainly used; The students of the experimental group (EG) were engaged in exercises including dance types of aerobics, callanetics, stretching, Pilates, and yoga. The experiment was carried out over the course of a semester (four months). Group classes were held twice a week as part of the hours of classes in “Physical Education (elective discipline)”. The cycle of classes ended with participation in an aerobics festival.
To assess the development of competencies in the discipline, a fund of assessment tools is created, which is a set of control and measurement materials (assessment tools) and methods of their use, intended to determine the level of student achievement of established learning outcomes.
When creating a fund of assessment tools for physical exercise, an effective system for monitoring physical fitness and development, physical health of students is necessary, the results of which allow the student to determine their level of physical fitness and develop individual programs aimed at correcting and creating a healthy lifestyle. To assess the level of physical fitness of students, exercises are used to demonstrate basic physical abilities: speed-strength endurance, static and dynamic strength, coordination, flexibility. These exercises should not differ significantly from
used in the practice of educational institutions to assess the level of physical fitness of high school graduates, as well as the standards of the GTO complex of the 5th and 6th stages (according to the age group).
At the first stage of our research, information was collected on the physical condition of female students, where it was revealed that indicators of the manifestation of physical qualities do not correspond to the age-sex norm; vital capacity of the lungs (VC) is 51.8% lower than the normal value; indicators of the level of physical performance and physical condition correspond to a low level.
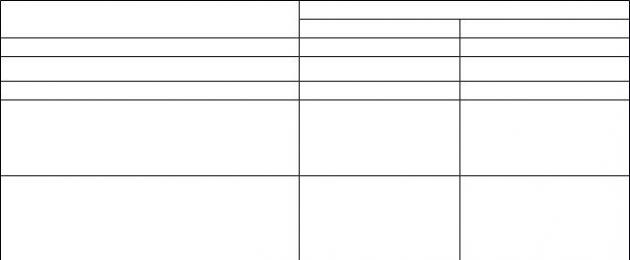
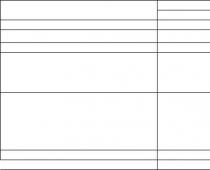
Indicators of changes in the level of physical fitness as a result of the conducted pedagogical experiment are presented in the table.
Indicators of changes in physical fitness of female students during a pedagogical experiment
Indicator Stages Groups Reliability
experi- X±t intergroup
ment differences
EG p=26 CG p=28 1 R
Aerobic endurance - “step test” (times/min) Beginning 83.51±3.6 79.5±3.6 1.713 >0.05
End 86.1±2.0 81.5±2.4 0.651 >0.05
1=2.54; p>0.05 1=0.68; p>0.05
Strength endurance Beginning 32.0±1.9 31.7±1.9 0.102 >0.05
- “lifting the body” End 37.3±1.7 36.3±1.6 0.414 >0.05
(times/min) 1=8.78; R<0,001 1=5,64; р<0,001
Strength endurance Beginning 21.7±1.7 20.5±2.3 0.420 >0.05
- “flexion of arms at the end 27.3±1.9 26.1±2.3 0.391 >0.05
lying position” (times/min) 1=2.22; R<0,001 1=5,57; р<0,001
Flexibility “forward bend” (cm) Beginning 12.3±1.4 13.7±1.6 0.643 >0.05
End 15.1±1.25 16.1±1.6 0.512 >0.05
1=12.88; R<0,001 1=4,16; р<0,001
In the experimental group, strength endurance of the arm muscles improved by 28% (p<0,001) и мышц брюшного пресса на 16 % (р<0,001), гибкость увеличилась на 22,2 % (р<0,001). Показатели аэробной выносливости улучшились на 5,6 % (р>0,05).
In the control group, strength endurance of the arm muscles improved by 27.6% (p<0,001) и мышц брюшного пресса на 14,5 % (р<0,001), гибкость увеличилась на 18 % (р<0,001). Незначительно изменились показатели аэробной выносливости (р>0.05), which is explained, in our opinion, by the short duration of the experiment.
As a result of conducting an elective course in physical education using physical education and health technologies for one semester in the control and experimental groups
the level of physical fitness has changed in a positive direction.
To study the influence of experimental classes on the emotional background of female students, before and after classes, at the beginning and at the end of the experiment, answer forms were filled out to determine self-esteem of reactive and personal anxiety.
The average indicator of personal anxiety in the groups of subjects was in the zone of average values (36-37 points). The reactive anxiety of female students at the beginning and end of the pedagogical experiment before the start of the lesson in our studies was also in the range of average values (36.9 and 37.1 points). This can be explained by a positive emotional attitude towards the upcoming health aerobics classes.
Indicators of reactive anxiety in the control and experimental groups in our experiment tend to decrease both during the lesson and during the experiment. In the experimental group these improvements were more pronounced. We did not find any statistically significant changes between the two groups, which we explain by the content of the classes, which are very similar in their impact on the emotional and motor spheres of the participants.
According to Yu.L. Khanina, only when dividing groups into high- and low-anxiety can reliable changes be identified when, by means of physical education, it is possible to optimize the emotional state of high-anxiety students.
A survey of female students at the end of the experiment showed that 90% of respondents had improved mood as a result of classes using physical education and health technologies, 78% indicated an improvement in overall well-being, 63% subjectively indicated body correction; The ability to move beautifully was influenced by classes for 56% of respondents; 41% acquired new knowledge about the basics of a healthy lifestyle and ways to maintain health; 12% of respondents acquired the ability to create complexes for independent exercise. Most of the students gladly participated in the aerobics festival with a test combination, which proves the feasibility of conducting final control in the discipline “Physical Education (elective discipline)” in a competitive form.
Students who completed the elective course unanimously supported the advisability of its introduction into the educational process of the university.
Thus, it can be argued that students, thanks to an elective course in physical education using physical culture and health technologies, increased their level of physical fitness, improved their emotional state, and formed specially targeted competencies in the field of physical education.
Bibliography
1. Reshetnikov N.V., Kislitsyn Yu.L. Physical culture: textbook. manual for students of the environment. prof. textbook establishments. M.: Masterstvo, 2002. 152 p.
2. Arvisto M.A. On the role and nature of value orientations in sports activities // Society and sport: collection of articles. scientific tr. M.: GCOLIFK, 1976. P. 6-14.
3. Vengerova, N.N., Kudashova L.T. Kinesiological construct of an elective course in physical education in higher education // European Social Science Journal (European Journal of Social Sciences). 2016. No. 4. pp. 238-243.
4. Batarshev A.V. Basic psychological properties and self-determination of personality: a practical guide to psychological diagnostics. St. Petersburg: Rech, 2005. pp. 44-49.
5. Khanin Yu.L., Bulanova G.V. Emotional well-being of students in sports and educational groups // Theory and practice of physics. culture. 1979. No. 4.
Kudashova Lyudmila Timofeevna, Ph.D. ped. Sciences, Associate Professor, worldlucy@,mail.ru, Russia, St. Petersburg, St. Petersburg State Economic University,
Vengerova Natalya Nikolaevna, Ph.D. ped. Sciences, Prof., natalyavengerova@yandex. ru, Russia, St. Petersburg, St. Petersburg State University of Economics
FORMATION OF COMPETENCE OF STUDENTS WITHIN THE ELECTIVE COURSES
FOR PHYSICAL CULTURE
L.T. Kudashova, N.N. Vengerova
Problems in the content of the elective course on physical culture with the aim of forming the general cultural competencies of students are revealed. The method of organization of the elective course on physical culture in the university with the use of physical culture and health technologies is presented. It takes into account the level of physical preparedness and emotional state of the students involved and promotes the formation of specially directed competencies among female students.
Key words: competence, elective course for physical education, sports and health technology, physical development, physical fitness.
Kudashova Lyudmila Timofeevna, candidate of pedagogical sciences, assistant professor, [email protected], Russia, Saint-Petersburg, Saint Petersburg State University of Economics,
Vengerova Natalia Nikolayevna, candidate of pedagogical sciences, professor, [email protected], Russia, Saint-Petersburg, Saint Petersburg State University of Economics
- In contact with 0
- Google+ 0
- OK 0
- Facebook 0