1) Copper nitrate was calcined, the resulting solid precipitate was dissolved in sulfuric acid. Hydrogen sulfide was passed through the solution, the resulting black precipitate was fired, and the solid residue was dissolved by heating in concentrated nitric acid.
2) Calcium phosphate was fused with coal and sand, then the resulting simple substance was burned in excess oxygen, the combustion product was dissolved in excess caustic soda. A barium chloride solution was added to the resulting solution. The resulting precipitate was treated with excess phosphoric acid.
| Show | |
|---|---|
Ca 3 (PO 4) 2 → P → P 2 O 5 → Na 3 PO 4 → Ba 3 (PO 4) 2 → BaHPO 4 or Ba(H 2 PO 4) 2 Ca 3 (PO 4) 2 + 5C + 3SiO 2 → 3CaSiO 3 + 2P + 5CO |
|
3) Copper was dissolved in concentrated nitric acid, the resulting gas was mixed with oxygen and dissolved in water. Zinc oxide was dissolved in the resulting solution, then a large excess of sodium hydroxide solution was added to the solution.
4) Dry sodium chloride was treated with concentrated sulfuric acid with low heating, the resulting gas was passed into a solution of barium hydroxide. A solution of potassium sulfate was added to the resulting solution. The resulting sediment was fused with coal. The resulting substance was treated with hydrochloric acid.
5) A sample of aluminum sulfide was treated with hydrochloric acid. At the same time, gas was released and a colorless solution was formed. An ammonia solution was added to the resulting solution, and the gas was passed through a lead nitrate solution. The resulting precipitate was treated with a solution of hydrogen peroxide.
| Show | |
|---|---|
Al(OH) 3 ←AlCl 3 ←Al 2 S 3 → H 2 S → PbS → PbSO 4 Al 2 S 3 + 6HCl → 3H 2 S + 2AlCl 3 |
|
6) Aluminum powder was mixed with sulfur powder, the mixture was heated, the resulting substance was treated with water, a gas was released and a precipitate was formed, to which an excess of potassium hydroxide solution was added until complete dissolution. This solution was evaporated and calcined. An excess of hydrochloric acid solution was added to the resulting solid.
7) A solution of potassium iodide was treated with a solution of chlorine. The resulting precipitate was treated with a solution of sodium sulfite. A solution of barium chloride was first added to the resulting solution, and after separation of the precipitate, a solution of silver nitrate was added.
8) Gray-green powder of chromium (III) oxide was fused with an excess of alkali, the resulting substance was dissolved in water, resulting in a dark green solution. Hydrogen peroxide was added to the resulting alkaline solution. The result is a yellow solution, which turns orange when sulfuric acid is added. When hydrogen sulfide is passed through the resulting acidified orange solution, it becomes cloudy and turns green again.
| Show | |
|---|---|
Cr 2 O 3 → KCrO 2 → K → K 2 CrO 4 → K 2 Cr 2 O 7 → Cr 2 (SO 4) 3 Cr 2 O 3 + 2KOH → 2KCrO 2 + H 2 O |
|
9) Aluminum was dissolved in a concentrated solution of potassium hydroxide. Carbon dioxide was passed through the resulting solution until the precipitation ceased. The precipitate was filtered and calcined. The resulting solid residue was fused with sodium carbonate.
10) Silicon was dissolved in a concentrated solution of potassium hydroxide. Excess hydrochloric acid was added to the resulting solution. The cloudy solution was heated. The resulting precipitate was filtered and calcined with calcium carbonate. Write the equations for the reactions described.
11) Copper(II) oxide was heated in a stream of carbon monoxide. The resulting substance was burned in a chlorine atmosphere. The reaction product was dissolved in water. The resulting solution was divided into two parts. A solution of potassium iodide was added to one part, and a solution of silver nitrate was added to the second. In both cases, the formation of a precipitate was observed. Write equations for the four reactions described.
12) Copper nitrate was calcined, the resulting solid was dissolved in dilute sulfuric acid. The solution of the resulting salt was subjected to electrolysis. The substance released at the cathode was dissolved in concentrated nitric acid. Dissolution proceeded with the release of brown gas. Write equations for the four reactions described.
13) Iron was burned in a chlorine atmosphere. The resulting substance was treated with an excess of sodium hydroxide solution. A brown precipitate formed, which was filtered and calcined. The residue after calcination was dissolved in hydroiodic acid. Write equations for the four reactions described.
14) Aluminum metal powder was mixed with solid iodine and a few drops of water were added. A solution of sodium hydroxide was added to the resulting salt until a precipitate formed. The resulting precipitate was dissolved in hydrochloric acid. Upon subsequent addition of sodium carbonate solution, precipitation was again observed. Write equations for the four reactions described.
15) As a result of incomplete combustion of coal, a gas was obtained, in the current of which iron(III) oxide was heated. The resulting substance was dissolved in hot concentrated sulfuric acid. The resulting salt solution was subjected to electrolysis. Write equations for the four reactions described.
16) A certain amount of zinc sulfide was divided into two parts. One of them was treated with nitric acid, and the other was fired in air. When the released gases interacted, a simple substance was formed. This substance was heated with concentrated nitric acid, and a brown gas was released. Write equations for the four reactions described.
17) Potassium chlorate was heated in the presence of a catalyst, and a colorless gas was released. By burning iron in an atmosphere of this gas, iron oxide was obtained. It was dissolved in excess hydrochloric acid. To the resulting solution was added a solution containing sodium dichromate and hydrochloric acid.
| Show | |
|---|---|
1) 2KClO 3 → 2KCl + 3O 2 2) ЗFe + 2O 2 → Fe 3 O 4 3) Fe 3 O 4 + 8НІ → FeCl 2 + 2FeCl 3 + 4H 2 O 4) 6 FeCl 2 + Na 2 Cr 2 O 7 + 14 HCI → 6 FeCl 3 + 2 CrCl 3 + 2NaCl + 7H 2 O 18) Iron was burned in chlorine. The resulting salt was added to the sodium carbonate solution, and a brown precipitate formed. This precipitate was filtered and calcined. The resulting substance was dissolved in hydroiodic acid. Write equations for the four reactions described. 1) 2Fe + 3Cl 2 → 2FeCl 3 2)2FeCl 3 +3Na 2 CO 3 →2Fe(OH) 3 +6NaCl+3CO 2 3) 2Fe(OH) 3 Fe 2 O 3 + 3H 2 O 4) Fe 2 O 3 + 6HI → 2FeI 2 + I 2 + 3H 2 O |
|
19) A solution of potassium iodide was treated with an excess of chlorine water, and first the formation of a precipitate was observed, and then its complete dissolution. The resulting iodine-containing acid was isolated from the solution, dried and carefully heated. The resulting oxide reacted with carbon monoxide. Write down the equations for the reactions described.
20) Chromium(III) sulfide powder was dissolved in sulfuric acid. At the same time, gas was released and a colored solution was formed. An excess of ammonia solution was added to the resulting solution, and the gas was passed through lead nitrate. The resulting black precipitate turned white after treatment with hydrogen peroxide. Write down the equations for the reactions described.
21) Aluminum powder was heated with sulfur powder, and the resulting substance was treated with water. The resulting precipitate was treated with an excess of a concentrated solution of potassium hydroxide until it was completely dissolved. A solution of aluminum chloride was added to the resulting solution and the formation of a white precipitate was again observed. Write down the equations for the reactions described.
22) Potassium nitrate was heated with powdered lead until the reaction stopped. The mixture of products was treated with water, and then the resulting solution was filtered. The filtrate was acidified with sulfuric acid and treated with potassium iodide. The isolated simple substance was heated with concentrated nitric acid. Red phosphorus was burned in the atmosphere of the resulting brown gas. Write down the equations for the reactions described.
23) Copper was dissolved in dilute nitric acid. An excess of ammonia solution was added to the resulting solution, observing first the formation of a precipitate, and then its complete dissolution with the formation of a dark blue solution. The resulting solution was treated with sulfuric acid until the characteristic blue color of copper salts appeared. Write down the equations for the reactions described.
| Show | |
|---|---|
1)3Cu+8HNO 3 →3Cu(NO 3) 2 +2NO+4H 2 O 2)Cu(NO 3) 2 +2NH 3 H 2 O→Cu(OH) 2 + 2NH 4 NO 3 3)Cu(OH) 2 +4NH 3 H 2 O →(OH) 2 + 4H 2 O 4)(OH) 2 +3H 2 SO 4 → CuSO 4 +2(NH 4) 2 SO 4 + 2H 2 O |
|
24) Magnesium was dissolved in dilute nitric acid, and no gas evolution was observed. The resulting solution was treated with an excess of potassium hydroxide solution while heating. The gas released was burned in oxygen. Write down the equations for the reactions described.
25) A mixture of potassium nitrite and ammonium chloride powders was dissolved in water and the solution was gently heated. The released gas reacted with magnesium. The reaction product was added to an excess of hydrochloric acid solution, and no gas evolution was observed. The resulting magnesium salt in solution was treated with sodium carbonate. Write down the equations for the reactions described.
26) Aluminum oxide was fused with sodium hydroxide. The reaction product was added to a solution of ammonium chloride. The released gas with a pungent odor is absorbed by sulfuric acid. The resulting medium salt was calcined. Write down the equations for the reactions described.
27) Chlorine reacted with a hot solution of potassium hydroxide. As the solution cooled, crystals of Berthollet salt precipitated. The resulting crystals were added to a solution of hydrochloric acid. The resulting simple substance reacted with metallic iron. The reaction product was heated with a new portion of iron. Write down the equations for the reactions described.
28) Copper was dissolved in concentrated nitric acid. An excess of ammonia solution was added to the resulting solution, observing first the formation of a precipitate, and then its complete dissolution. The resulting solution was treated with excess hydrochloric acid. Write down the equations for the reactions described.
29) Iron was dissolved in hot concentrated sulfuric acid. The resulting salt was treated with an excess of sodium hydroxide solution. The brown precipitate that formed was filtered and calcined. The resulting substance was fused with iron. Write equations for the four reactions described.
30) As a result of incomplete combustion of coal, a gas was obtained, in the current of which iron(III) oxide was heated. The resulting substance was dissolved in hot concentrated sulfuric acid. The resulting salt solution was treated with an excess of potassium sulfide solution.
31) A certain amount of zinc sulfide was divided into two parts. One of them was treated with hydrochloric acid, and the other was fired in air. When the released gases interacted, a simple substance was formed. This substance was heated with concentrated nitric acid, and a brown gas was released.
32) Sulfur was fused with iron. The reaction product was treated with hydrochloric acid. The gas released was burned in excess oxygen. The combustion products were absorbed by an aqueous solution of iron(III) sulfate.
1 . Sodium was burned in excess oxygen, the resulting crystalline substance was placed in a glass tube and carbon dioxide was passed through it. The gas coming out of the tube was collected and phosphorus was burned in its atmosphere. The resulting substance was neutralized with an excess of sodium hydroxide solution.
1) 2Na + O 2 = Na 2 O 2
2) 2Na 2 O 2 + 2CO 2 = 2Na 2 CO 3 + O 2
3) 4P + 5O 2 = 2P 2 O 5
4) P 2 O 5 + 6 NaOH = 2Na 3 PO 4 + 3H 2 O
2. Aluminum carbide was treated with hydrochloric acid. The released gas was burned, the combustion products were passed through lime water until a white precipitate was formed, further passing the combustion products into the resulting suspension led to the dissolution of the precipitate.
1) Al 4 C 3 + 12HCl = 3CH 4 + 4AlCl 3
2) CH 4 + 2O 2 = CO 2 + 2H 2 O
3) CO 2 + Ca(OH) 2 = CaCO 3 + H 2 O
4) CaCO 3 + H 2 O + CO 2 = Ca(HCO 3) 2
3. Pyrite was fired, the resulting gas with a pungent odor was passed through hydrosulfide acid. The resulting yellowish precipitate was filtered, dried, mixed with concentrated nitric acid and heated. The resulting solution gives a precipitate containing barium nitrate.
1) 4FeS 2 + 11O 2 → 2Fe 2 O 3 + 8SO 2
2) SO 2 + 2H 2 S = 3S + 2H 2 O
3) S+ 6HNO 3 = H 2 SO 4 + 6NO 2 +2H 2 O
4) H 2 SO 4 + Ba(NO 3) 2 = BaSO 4 ↓ + 2 HNO 3
4 . The copper was placed in concentrated nitric acid, the resulting salt was isolated from the solution, dried and calcined. The solid reaction product was mixed with copper shavings and calcined in an inert gas atmosphere. The resulting substance was dissolved in ammonia water.
1) Cu + 4HNO 3 = Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2NO 2 +2H 2 O
2) 2Cu(NO 3) 2 = 2CuO + 4NO 2 + O 2
3) Cu + CuO = Cu 2 O
4) Cu 2 O + 4NH 3 + H 2 O = 2OH
5 . Iron filings were dissolved in dilute sulfuric acid, and the resulting solution was treated with an excess of sodium hydroxide solution. The resulting precipitate was filtered and left in air until it acquired a brown color. The brown substance was calcined to constant mass.
1) Fe + H 2 SO 4 = FeSO 4 + H 2
2) FeSO 4 + 2NaOH = Fe(OH) 2 + Na 2 SO 4
3) 4Fe(OH) 2 + 2H 2 O + O 2 = 4Fe(OH) 3
4) 2Fe(OH) 3 = Fe 2 O 3 + 3H 2 O
6 . Zinc sulfide was calcined. The resulting solid reacted completely with the potassium hydroxide solution. Carbon dioxide was passed through the resulting solution until a precipitate formed. The precipitate was dissolved in hydrochloric acid.
1) 2ZnS + 3O 2 = 2ZnO + 2SO 2
2) ZnO + 2NaOH + H 2 O = Na 2
3 Na 2 + CO 2 = Na 2 CO 3 + H 2 O + Zn(OH) 2
4) Zn(OH) 2 + 2 HCl = ZnCl 2 + 2H 2 O
7. The gas released when zinc reacted with hydrochloric acid was mixed with chlorine and exploded. The resulting gaseous product was dissolved in water and acted on manganese dioxide. The resulting gas was passed through a hot solution of potassium hydroxide.
1) Zn+ 2HCl = ZnCl 2 + H 2
2) Cl 2 + H 2 = 2HCl
3) 4HCl + MnO 2 = MnCl 2 + 2H 2 O + Cl 2
4) 3Cl 2 + 6KOH = 5KCl + KClO 3 + 3H 2 O
8. Calcium phosphide was treated with hydrochloric acid. The released gas was burned in a closed vessel, and the combustion product was completely neutralized with a solution of potassium hydroxide. A solution of silver nitrate was added to the resulting solution.
1) Ca 3 P 2 + 6HCl = 3CaCl 2 + 2PH 3
2) PH 3 + 2O 2 = H 3 PO 4
3) H 3 PO 4 + 3KOH = K 3 PO 4 + 3H 2 O
4) K 3 PO 4 + 3AgNO 3 = 3KNO 3 + Ag 3 PO 4
9 . Ammonium dichromate decomposed when heated. The solid decomposition product was dissolved in sulfuric acid. A solution of sodium hydroxide was added to the resulting solution until a precipitate formed. Upon further addition of sodium hydroxide to the precipitate, it dissolved.
1) (NH 4) 2 Cr 2 O 7 = Cr 2 O 3 + N 2 + 4H 2 O
2) Cr 2 O 3 + 3H 2 SO 4 = Cr 2 (SO 4) 3 + 3H 2 O
3) Cr 2 (SO 4) 3 + 6NaOH = 3Na 2 SO 4 + 2Cr(OH) 3
4) 2Cr(OH) 3 + 3NaOH = Na 3
10 . Calcium orthophosphate was calcined with coal and river sand. The resulting white glow-in-the-dark substance was burned in a chlorine atmosphere. The product of this reaction was dissolved in excess potassium hydroxide. A solution of barium hydroxide was added to the resulting mixture.
1) Ca 3 (PO 4) 2 + 5C + 3SiO 2 = 3CaSiO 3 + 5CO + 2P
2) 2P + 5Cl 2 = 2PCl 5
3) PCl 5 + 8KOH = K 3 PO 4 + 5KCl + 4H 2 O
4) 2K 3 PO 4 + 3Ba(OH) 2 = Ba 3 (PO 4) 2 + 6KOH
11. Aluminum powder was mixed with sulfur and heated. The resulting substance was placed in water. The resulting precipitate was divided into two parts. Hydrochloric acid was added to one part, and sodium hydroxide solution was added to the other until the precipitate was completely dissolved.
1) 2Al + 3S = Al 2 S 3
2) Al 2 S 3 + 6H 2 O = 2Al(OH) 3 + 3H 2 S
3) Al(OH) 3 + 3HCl= AlCl 3 + 3H 2 O
4) Al(OH) 3 + NaOH = Na
12 . Silicon was placed in a solution of potassium hydroxide, and after the reaction was completed, excess hydrochloric acid was added to the resulting solution. The precipitate that formed was filtered, dried and calcined. The solid calcination product reacts with hydrogen fluoride.
1) Si + 2KOH + H 2 O = K 2 SiO 3 + 2H 2
2) K 2 SiO 3 + 2HCl = 2KCl + H 2 SiO 3
3) H 2 SiO 3 = SiO 2 + H 2 O
4) SiO 2 + 4HF = SiF 4 + 2H 2 O
Tasks for independent solution.
1. As a result of the thermal decomposition of ammonium dichromate, a gas was obtained, which was passed over heated magnesium. The resulting substance was placed in water. The resulting gas was passed through freshly precipitated copper(II) hydroxide. Write the equations for the reactions described.
2. A solution of hydrochloric acid was added to the solution obtained by reacting sodium peroxide with water when heated until the reaction was completed. The solution of the resulting salt was subjected to electrolysis with inert electrodes. The gas formed as a result of electrolysis at the anode was passed through a suspension of calcium hydroxide. Write the equations for the reactions described.
3. The precipitate formed as a result of the interaction of a solution of iron(II) sulfate and sodium hydroxide was filtered and calcined. The solid residue was completely dissolved in concentrated nitric acid. Copper shavings were added to the resulting solution. Write the equations for the reactions described.
4. The gas produced by roasting pyrite reacted with hydrogen sulfide. The yellow substance obtained as a result of the reaction was treated with concentrated nitric acid while heating. A solution of barium chloride was added to the resulting solution. Write the equations for the reactions described.
5. The gas obtained by reacting iron filings with a solution of hydrochloric acid was passed over heated copper (II) oxide until the metal was completely reduced. The resulting metal was dissolved in concentrated nitric acid. The resulting solution was subjected to electrolysis with inert electrodes. Write the equations for the reactions described.
6. The gas released at the anode during the electrolysis of mercury(II) nitrate was used for the catalytic oxidation of ammonia. The resulting colorless gas instantly reacted with oxygen in the air. The resulting brown gas was passed through barite water. Write the equations for the reactions described.
7. Iodine was placed in a test tube with concentrated hot nitric acid. The released gas was passed through water in the presence of oxygen. Copper(II) hydroxide was added to the resulting solution. The resulting solution was evaporated and the dry solid residue was calcined. Write the equations for the reactions described.
8. When a solution of aluminum sulfate reacted with a solution of potassium sulfide, a gas was released, which was passed through a solution of potassium hexahydroxyaluminate. The resulting precipitate was filtered, washed, dried and heated. The solid residue was fused with caustic soda. Write the equations for the reactions described.
9. Sulfur dioxide was passed through a solution of sodium hydroxide until a medium salt was formed. An aqueous solution of potassium permanganate was added to the resulting solution. The resulting precipitate was separated and treated with hydrochloric acid. The released gas was passed through a cold solution of potassium hydroxide. Write the equations for the reactions described.
10. A mixture of silicon(IV) oxide and metallic magnesium was calcined. The simple substance obtained as a result of the reaction was treated with a concentrated solution of sodium hydroxide. The released gas was passed over heated sodium. The resulting substance was placed in water. Write the equations for the reactions described.
Topic 7. Chemical properties and receiving organic matter in tasks C3. Reactions that cause the greatest difficulties in schoolchildren that go beyond the scope of the school course.
To solve C3 tasks, schoolchildren need to know the entire organic chemistry course at a specialized level.
Task No. 1
Sodium was heated in a hydrogen atmosphere. When water was added to the resulting substance, gas evolution and the formation of a clear solution were observed. Brown gas was passed through this solution, which was obtained as a result of the interaction of copper with a concentrated solution of nitric acid. Write equations for the four reactions described.
1) When sodium is heated in a hydrogen atmosphere (T = 250-400 o C), sodium hydride is formed:
2Na + H 2 = 2NaH
2) When water is added to sodium hydride, an alkali NaOH is formed and hydrogen is released:
NaH + H 2 O = NaOH + H 2
3) When copper reacts with a concentrated solution of nitric acid, brown gas is released - NO 2:
Cu + 4HNO 3 (conc.) = Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2NO 2 + 2H 2 O
4) When brown gas NO 2 is passed through an alkali solution, a disproportionation reaction occurs - nitrogen N +4 is simultaneously oxidized and reduced to N +5 and N +3:
2NaOH + 2NO2 = NaNO3 + NaNO2 + H2O
(disproportionation reaction 2N +4 → N +5 + N +3).
Task No. 2
Iron scale was dissolved in concentrated nitric acid. A sodium hydroxide solution was added to the resulting solution. The resulting precipitate was separated and calcined. The resulting solid residue was fused with iron. Write equations for the four reactions described.
The formula of iron scale is Fe 3 O 4.
When iron scale interacts with concentrated nitric acid, iron nitrate is formed and nitrogen oxide NO 2 is released:
Fe 3 O 4 + 10HNO 3 (conc.) → 3Fe (NO 3) 3 + NO 2 + 5H 2 O
When iron nitrate reacts with sodium hydroxide, a precipitate is released - iron (III) hydroxide:
Fe(NO 3) 3 + 3NaOH → Fe(OH) 3 ↓ + 3NaNO 3
Fe(OH) 3 is an amphoteric hydroxide, insoluble in water, decomposes when heated into iron (III) oxide and water:
2Fe(OH) 3 → Fe 2 O 3 + 3H 2 O
When iron(III) oxide fuses with iron, iron(II) oxide is formed:
Fe 2 O 3 + Fe → 3FeO
Task No. 3
The sodium was burned in air. The resulting substance was treated with hydrogen chloride when heated. The resulting simple yellow-green substance, when heated, reacted with chromium (III) oxide in the presence of potassium hydroxide. When a solution of one of the resulting salts was treated with barium chloride, a yellow precipitate formed. Write equations for the four reactions described.
1) When sodium is burned in air, sodium peroxide is formed:
2Na + O 2 → Na 2 O 2
2) When sodium peroxide reacts with hydrogen chloride when heated, Cl 2 gas is released:
Na 2 O 2 + 4HCl → 2NaCl + Cl 2 + 2H 2 O
3) In an alkaline environment, chlorine reacts when heated with amphoteric chromium oxide to form chromate and potassium chloride:
Cr 2 O 3 + 3Cl 2 + 10KOH → 2K 2 CrO 4 + 6KCl + 5H 2 O
2Cr +3 -6e → 2Cr +6 | . 3 - oxidation
Cl 2 + 2e → 2Cl − | . 1 - recovery
4) A yellow precipitate (BaCrO 4) is formed by the interaction of potassium chromate and barium chloride:
K 2 CrO 4 + BaCl 2 → BaCrO 4 ↓ + 2KCl
Task No. 4
Zinc is completely dissolved in a concentrated solution of potassium hydroxide. The resulting clear solution was evaporated and then calcined. The solid residue was dissolved in the required amount of hydrochloric acid. Ammonium sulfide was added to the resulting clear solution and the formation of a white precipitate was observed. Write equations for the four reactions described.
1) Zinc reacts with potassium hydroxide to form potassium tetrahydroxocinate (Al and Be behave similarly):
2) After calcination, potassium tetrahydroxozincate loses water and turns into potassium zincate:
3) Potassium zincate, when reacting with hydrochloric acid, forms zinc chloride, potassium chloride and water:
4) Zinc chloride, as a result of interaction with ammonium sulfide, turns into insoluble zinc sulfide - a white precipitate:
Task No. 5
Hydroiodic acid was neutralized with potassium bicarbonate. The resulting salt reacted with a solution containing potassium dichromate and sulfuric acid. When the resulting simple substance reacted with aluminum, a salt was obtained. This salt was dissolved in water and mixed with a solution of potassium sulfide, resulting in the formation of a precipitate and the release of gas. Write equations for the four reactions described.
1) Hydroiodic acid is neutralized by the acid salt of weak carbonic acid, resulting in the release of carbon dioxide and the formation of NaCl:
HI + KHCO 3 → KI + CO 2 + H 2 O
2) Potassium iodide enters into a redox reaction with potassium dichromate in an acidic environment, while Cr +6 is reduced to Cr +3, I - is oxidized to molecular I 2, which precipitates:
6KI + K 2 Cr 2 O 7 + 7H 2 SO 4 → Cr 2 (SO 4) 3 + 4K 2 SO 4 + 3I 2 ↓ + 7H 2 O
2Cr +6 + 6e → 2Cr +3 │ 1
2I − -2e → I 2 │ 3
3) When molecular iodine reacts with aluminum, aluminum iodide is formed:
2Al + 3I 2 → 2AlI 3
4) When aluminum iodide reacts with a solution of potassium sulfide, Al(OH) 3 precipitates and H 2 S is released. The formation of Al 2 S 3 does not occur due to complete hydrolysis of the salt in an aqueous solution:
2AlI 3 + 3K 2 S + 6H 2 O → 2Al(OH) 3 ↓ + 6KI + 3H 2 S
Task No. 6
Aluminum carbide was completely dissolved in hydrobromic acid. A solution of potassium sulfite was added to the resulting solution, and the formation of a white precipitate and the evolution of a colorless gas were observed. The gas was absorbed by a solution of potassium dichromate in the presence of sulfuric acid. The resulting chromium salt was isolated and added to the barium nitrate solution, and the formation of a precipitate was observed. Write equations for the four reactions described.
1) When aluminum carbide is dissolved in hydrobromic acid, a salt is formed - aluminum bromide, and methane is released:
Al 4 C 3 + 12HBr → 4AlBr 3 + 3CH 4
2) When aluminum bromide reacts with a solution of potassium sulfite, Al(OH) 3 precipitates and sulfur dioxide is released - SO 2:
2AlBr 3 + 3K 2 SO 3 + 3H 2 O → 2Al(OH) 3 ↓ + 6KBr + 3SO 2
3) By passing sulfur dioxide through an acidified solution of potassium dichromate, Cr +6 is reduced to Cr +3, S +4 is oxidized to S +6:
3SO 2 + K 2 Cr 2 O 7 + H 2 SO 4 → Cr 2 (SO 4) 3 + K 2 SO 4 + H 2 O
2Cr +6 + 6e → 2Cr +3 │ 1
S +4 -2e → S +6 │ 3
4) When chromium (III) sulfate reacts with a solution of barium nitrate, chromium (III) nitrate is formed, and white barium sulfate precipitates:
Cr 2 (SO 4) 3 + 3Ba(NO 3) 2 → 3BaSO 4 ↓ + 2Cr(NO 3) 3
Task No. 7
Aluminum powder was added to the sodium hydroxide solution. Excess carbon dioxide was passed through the solution of the resulting substance. The precipitate that formed was separated and calcined. The resulting product was fused with sodium carbonate. Write equations for the four reactions described.
1) Aluminum, as well as beryllium and zinc, is capable of reacting with both aqueous solutions of alkalis and anhydrous alkalis during fusion. When aluminum is treated with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide, sodium tetrahydroxyaluminate and hydrogen are formed:
2) When carbon dioxide is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium tetrahydroxoaluminate, crystalline aluminum hydroxide precipitates. Since, according to the condition, an excess of carbon dioxide is passed through the solution, it is not carbonate that is formed, but sodium bicarbonate:
Na + CO 2 → Al(OH) 3 ↓ + NaHCO 3
3) Aluminum hydroxide is an insoluble metal hydroxide, therefore, when heated, it decomposes into the corresponding metal oxide and water:
4) Aluminum oxide, which is an amphoteric oxide, when fused with carbonates, displaces carbon dioxide from them to form aluminates (not to be confused with tetrahydroxoaluminates!):
Task No. 8
Aluminum reacted with sodium hydroxide solution. The released gas was passed over heated copper (II) oxide powder. The resulting simple substance was dissolved by heating in concentrated sulfuric acid. The resulting salt was isolated and added to the potassium iodide solution. Write equations for the four reactions described.
1) Aluminum (also beryllium and zinc) reacts with both aqueous solutions of alkalis and anhydrous alkalis when fused. When aluminum is treated with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide, sodium tetrahydroxyaluminate and hydrogen are formed:
2NaOH + 2Al + 6H 2 O → 2Na + 3H 2
2) When hydrogen is passed over heated copper (II) oxide powder, Cu +2 is reduced to Cu 0: the color of the powder changes from black (CuO) to red (Cu):
3) Copper dissolves in concentrated sulfuric acid to form copper (II) sulfate. In addition, sulfur dioxide is released:
4) When copper sulfate is added to a solution of potassium iodide, an oxidation-reduction reaction occurs: Cu +2 is reduced to Cu +1, I - is oxidized to I 2 (molecular iodine precipitates):
CuSO 4 + 4KI → 2CuI + 2K 2 SO 4 + I 2 ↓
Task No. 9
We carried out electrolysis of a sodium chloride solution. Iron (III) chloride was added to the resulting solution. The precipitate that formed was filtered and calcined. The solid residue was dissolved in hydroiodic acid. Write equations for the four reactions described.
1) Electrolysis of sodium chloride solution:
Cathode: 2H 2 O + 2e → H 2 + 2OH −
Anode: 2Cl − − 2e → Cl 2
Thus, as a result of its electrolysis, gaseous H 2 and Cl 2 are released from a sodium chloride solution, and Na + and OH − ions remain in the solution. In general, the equation is written as follows:
2H 2 O + 2NaCl → H 2 + 2NaOH + Cl 2
2) When iron (III) chloride is added to an alkali solution, an exchange reaction occurs, as a result of which Fe(OH) 3 precipitates:
3NaOH + FeCl 3 → Fe(OH) 3 ↓ + 3NaCl
3) When iron (III) hydroxide is calcined, iron (III) oxide and water are formed:
4) When iron (III) oxide is dissolved in hydroiodic acid, FeI 2 is formed, while I 2 precipitates:
Fe 2 O 3 + 6HI → 2FeI 2 + I 2 ↓ + 3H 2 O
2Fe +3 + 2e → 2Fe +2 │1
2I − − 2e → I 2 │1
Task No. 10
Potassium chlorate was heated in the presence of a catalyst, releasing a colorless gas. By burning iron in an atmosphere of this gas, iron oxide was obtained. It was dissolved in excess hydrochloric acid. To the resulting solution was added a solution containing sodium dichromate and hydrochloric acid.
1) When potassium chlorate is heated in the presence of a catalyst (MnO 2, Fe 2 O 3, CuO, etc.), potassium chloride is formed and oxygen is released:
2) When iron is burned in an oxygen atmosphere, iron scale is formed, the formula of which is Fe 3 O 4 (iron scale is a mixed oxide of Fe 2 O 3 and FeO):
3) When iron scale is dissolved in excess hydrochloric acid, a mixture of iron (II) and (III) chlorides is formed:
4) In the presence of a strong oxidizing agent - sodium dichromate, Fe +2 is oxidized to Fe +3:
6FeCl 2 + Na 2 Cr 2 O 7 + 14HCl → 6FeCl 3 + 2CrCl 3 + 2NaCl + 7H 2 O
Fe +2 – 1e → Fe +3 │6
2Cr +6 + 6e → 2Cr +3 │1
Task No. 11
Ammonia was passed through hydrobromic acid. A solution of silver nitrate was added to the resulting solution. The precipitate that formed was separated and heated with zinc powder. The metal formed during the reaction was exposed to a concentrated solution of sulfuric acid, which released a gas with a pungent odor. Write equations for the four reactions described.
1) When ammonia is passed through hydrobromic acid, ammonium bromide is formed (neutralization reaction):
NH 3 + HBr → NH 4 Br
2) When solutions of ammonium bromide and silver nitrate are combined, an exchange reaction occurs between the two salts, resulting in the formation of a light yellow precipitate - silver bromide:
NH 4 Br + AgNO 3 → AgBr↓ + NH 4 NO 3
3) When silver bromide is heated with zinc powder, a substitution reaction occurs - silver is released:
2AgBr + Zn → 2Ag + ZnBr 2
4) When concentrated sulfuric acid acts on metal, silver sulfate is formed and a gas with an unpleasant odor is released - sulfur dioxide:
2Ag + 2H 2 SO 4 (conc.) → Ag 2 SO 4 + SO 2 + 2H 2 O
2Ag 0 – 2e → 2Ag + │1
S +6 + 2e → S +4 │1
Task No. 12
9С278С
Chromium(VI) oxide reacted with potassium hydroxide. The resulting substance was treated with sulfuric acid, and an orange salt was isolated from the resulting solution. This salt was treated with hydrobromic acid. The resulting simple substance reacted with hydrogen sulfide. Write equations for the four reactions described.
1) Chromium (VI) oxide CrO 3 is an acidic oxide, therefore, it reacts with alkali to form a salt - potassium chromate:
CrO 3 + 2KOH → K 2 CrO 4 + H 2 O
2) Potassium chromate in an acidic environment is converted without changing the oxidation state of chromium into dichromate K 2 Cr 2 O 7 - an orange salt:
2K 2 CrO 4 + H 2 SO 4 → K 2 Cr 2 O 7 + K 2 SO 4 + H 2 O
3) When treating potassium dichromate with hydrobromic acid, Cr +6 is reduced to Cr +3, and molecular bromine is released:
K 2 Cr 2 O 7 + 14HBr → 2CrBr 3 + 2KBr + 3Br 2 + 7H 2 O
2Cr +6 + 6e → 2Cr +3 │1
2Br − − 2e → Br 2 │3
4) Bromine, as a stronger oxidizing agent, displaces sulfur from it hydrogen connection:
Br 2 + H 2 S → 2HBr + S↓
Task No. 13
Magnesium powder was heated in a nitrogen atmosphere. When the resulting substance interacted with water, a gas was released. The gas was passed through an aqueous solution of chromium(III) sulfate, resulting in the formation of a gray precipitate. The precipitate was separated and treated by heating with a solution containing hydrogen peroxide and potassium hydroxide. Write equations for the four reactions described.
1) When magnesium powder is heated in a nitrogen atmosphere, magnesium nitride is formed:
2) Magnesium nitride is completely hydrolyzed to form magnesium hydroxide and ammonia:
Mg 3 N 2 + 6H 2 O → 3Mg(OH) 2 ↓ + 2NH 3
3) Ammonia has basic properties due to the presence of a lone electron pair on the nitrogen atom and, as a base, enters into an exchange reaction with chromium (III) sulfate, as a result of which a gray precipitate is released - Cr(OH) 3:
6NH3. H 2 O + Cr 2 (SO 4) 3 → 2Cr(OH) 3 ↓ + 3(NH 4) 2 SO 4
4) Hydrogen peroxide in an alkaline environment oxidizes Cr +3 to Cr +6, resulting in the formation of potassium chromate:
2Cr(OH) 3 + 3H 2 O 2 + 4KOH → 2K 2 CrO 4 + 8H 2 O
Cr +3 -3e → Cr +6 │2
2O − + 2e → 2O -2 │3
Task No. 14
When aluminum oxide reacted with nitric acid, a salt was formed. The salt was dried and calcined. The solid residue formed during calcination was subjected to electrolysis in molten cryolite. The metal obtained by electrolysis was heated with a concentrated solution containing potassium nitrate and potassium hydroxide, and a gas with a pungent odor was released. Write equations for the four reactions described.
1) When amphoteric Al 2 O 3 interacts with nitric acid, a salt is formed - aluminum nitrate (exchange reaction):
Al 2 O 3 + 6HNO 3 → 2Al(NO 3) 3 + 3H 2 O
2) When aluminum nitrate is calcined, aluminum oxide is formed, and nitrogen dioxide and oxygen are also released (aluminum belongs to the group of metals (in the activity series from alkaline earth to Cu inclusive), the nitrates of which decompose to metal oxides, NO 2 and O 2):
3) Metallic aluminum is formed during the electrolysis of Al 2 O 3 in molten cryolite Na 2 AlF 6 at 960-970 o C.
Al 2 O 3 electrolysis scheme:
Dissociation of aluminum oxide occurs in the melt:
Al 2 O 3 → Al 3+ + AlO 3 3-
K(-): Al 3+ + 3e → Al 0
A(+): 4AlO 3 3- − 12e → 2Al 2 O 3 + 3O 2
Overall process equation:
Liquid aluminum collects at the bottom of the electrolyser.
4) When aluminum is treated with a concentrated alkaline solution containing potassium nitrate, ammonia is released and potassium tetrahydroxyaluminate is also formed (alkaline medium):
8Al + 5KOH + 3KNO 3 + 18H 2 O → 3NH 3 + 8K
Al 0 – 3e → Al +3 │8
N +5 + 8e → N -3 │3
Task No. 15
8AAA8C
Some iron(II) sulfide was divided into two parts. One of them was treated with hydrochloric acid, and the other was fired in air. When the released gases interacted, a simple yellow substance was formed. The resulting substance was heated with concentrated nitric acid, and a brown gas was released. Write equations for the four reactions described.
1) When iron (II) sulfide is treated with hydrochloric acid, iron (II) chloride is formed and hydrogen sulfide is released (exchange reaction):
FeS + 2HCl → FeCl 2 + H 2 S
2) When burning iron (II) sulfide, iron is oxidized to the oxidation state +3 (Fe 2 O 3 is formed) and sulfur dioxide is released:
3) When two sulfur-containing compounds SO 2 and H 2 S interact, an oxidation-reduction reaction (coproportionation) occurs, as a result of which sulfur is released:
2H 2 S + SO 2 → 3S↓ + 2H 2 O
S -2 – 2e → S 0 │2
S +4 + 4e → S 0 │1
4) When sulfur is heated with concentrated nitric acid, it forms sulfuric acid and nitrogen dioxide (redox reaction):
S + 6HNO 3 (conc.) → H 2 SO 4 + 6NO 2 + 2H 2 O
S 0 – 6e → S +6 │1
N +5 + e → N +4 │6
Task No. 16
The gas obtained by treating calcium nitride with water was passed over hot copper (II) oxide powder. The resulting solid was dissolved in concentrated nitric acid, the solution was evaporated, and the resulting solid residue was calcined. Write down equations for the four reactions described.
1) Calcium nitride reacts with water, forming alkali and ammonia:
Ca 3 N 2 + 6H 2 O → 3Ca(OH) 2 + 2NH 3
2) By passing ammonia over a hot powder of copper (II) oxide, the copper in the oxide is reduced to metallic, and nitrogen is released (hydrogen, coal, carbon monoxide, etc. are also used as reducing agents):
Cu +2 + 2e → Cu 0 │3
2N -3 – 6e → N 2 0 │1
3) Copper, located in the series of metal activities after hydrogen, reacts with concentrated nitric acid to form copper nitrate and nitrogen dioxide:
Cu + 4HNO 3(conc.) → Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2NO 2 + 2H 2 O
Cu 0 - 2e → Cu +2 │1
N +5 +e → N +4 │2
4) When copper nitrate is calcined, copper oxide is formed, and nitrogen dioxide and oxygen are also released (copper belongs to the group of metals (in the activity series from alkaline earth to Cu inclusive), the nitrates of which decompose to metal oxides, NO 2 and O 2):
Task No. 17
Silicon was burned in a chlorine atmosphere. The resulting chloride was treated with water. The precipitate released was calcined. Then fused with calcium phosphate and coal. Write down equations for the four reactions described.
1) The reaction between silicon and chlorine occurs at a temperature of 340-420 o C in a flow of argon with the formation of silicon (IV) chloride:
2) Silicon (IV) chloride is completely hydrolyzed, resulting in the formation of hydrochloric acid, and silicic acid precipitates:
SiCl 4 + 3H 2 O → H 2 SiO 3 ↓ + 4HCl
3) When calcined, silicic acid decomposes to silicon (IV) oxide and water:
4) When silicon dioxide is fused with coal and calcium phosphate, an oxidation-reduction reaction occurs, resulting in the formation of calcium silicate, phosphorus, and the release of carbon monoxide:
C 0 − 2e → C +2 │10
4P +5 +20e → P 4 0 │1
Task No. 18
Note! This format of tasks is outdated, but nevertheless tasks of this type deserve attention, since in fact they require writing down the same equations that are found in KIMakh Unified State Examination new format.
The following substances are given: iron, iron scale, dilute hydrochloric and concentrated nitric acid. Write equations for four possible reactions between all the proposed substances, without repeating pairs of reactants.
1) Hydrochloric acid reacts with iron, oxidizing it to the oxidation state +2, and hydrogen is released (substitution reaction):
Fe + 2HCl → FeCl 2 + H 2
2) Concentrated nitric acid passivates iron (i.e., a strong protective oxide film is formed on its surface), but under the influence high temperature iron is oxidized with concentrated nitric acid to oxidation state +3:
3) The formula of iron scale is Fe 3 O 4 (a mixture of iron oxides FeO and Fe 2 O 3). Fe 3 O 4 enters into an exchange reaction with hydrochloric acid, resulting in a mixture of two iron (II) and (III) chlorides:
Fe 3 O 4 + 8HCl → 2FeCl 3 + FeCl 2 + 4H 2 O
4) In addition, iron scale enters into a redox reaction with concentrated nitric acid, and the Fe +2 contained in it is oxidized to Fe +3:
Fe 3 O 4 + 10HNO 3 (conc.) → 3Fe(NO 3) 3 + NO 2 + 5H 2 O
5) Iron scale and iron, when sintered, enter into a comporportionation reaction (the same oxidizing agent and reducing agent chemical element):
Task No. 19
The following substances are given: phosphorus, chlorine, aqueous solutions of sulfuric acid and potassium hydroxide. Write equations for four possible reactions between all the proposed substances, without repeating pairs of reactants.
1) Chlorine is a poisonous gas with high chemical activity and reacts especially vigorously with red phosphorus. In an atmosphere of chlorine, phosphorus spontaneously ignites and burns with a weak greenish flame. Depending on the ratio of the reactants, phosphorus (III) chloride or phosphorus (V) chloride can be obtained:
2P (red) + 3Cl 2 → 2PCl 3
2P (red) + 5Cl 2 → 2PCl 5
Cl 2 + 2KOH → KCl + KClO + H 2 O
If chlorine is passed through a hot concentrated alkali solution, the molecular chlorine is disproportionated into Cl +5 and Cl -1, resulting in the formation of chlorate and chloride, respectively:
3) As a result of the interaction of aqueous solutions of alkali and sulfuric acid, an acidic or average salt of sulfuric acid is formed (depending on the concentration of the reagents):
KOH + H2SO4 → KHSO4 + H2O
2KOH + H 2 SO 4 → K 2 SO 4 + 2H 2 O (neutralization reaction)
4) Strong oxidizing agents such as sulfuric acid convert phosphorus into phosphoric acid:
2P + 5H 2 SO 4 → 2H 3 PO 4 + 5SO 2 + 2H 2 O
Task No. 20
The substances given are: nitric oxide (IV), copper, potassium hydroxide solution and concentrated sulfuric acid. Write equations for four possible reactions between all the proposed substances, without repeating pairs of reactants.
1) Copper, located in the series of metal activities to the right of hydrogen, is capable of oxidation by strong oxidizing acids (H 2 SO 4 (conc.), HNO 3, etc.):
Cu + 2H 2 SO 4 (conc.) → CuSO 4 + SO 2 + 2H 2 O
2) As a result of the interaction of a KOH solution with concentrated sulfuric acid, an acid salt is formed - potassium hydrogen sulfate:
KOH + H 2 SO 4 (conc.) → KHSO 4 + H 2 O
3) When passing brown gas, NO 2 N +4 is disproportioned into N +5 and N +3, resulting in the formation of potassium nitrate and nitrite, respectively:
2NO 2 + 2KOH → KNO 3 + KNO 2 + H 2 O
4) When brown gas is passed through a concentrated solution of sulfuric acid, N +4 is oxidized to N +5 and sulfur dioxide is released:
2NO 2 + H 2 SO 4 (conc.) → 2HNO 3 + SO 2
Task No. 21
The following substances are given: chlorine, sodium hydrosulfide, potassium hydroxide (solution), iron. Write equations for four possible reactions between all the proposed substances, without repeating pairs of reactants.
1) Chlorine, being a strong oxidizing agent, reacts with iron, oxidizing it to Fe +3:
2Fe + 3Cl 2 → 2FeCl 3
2) When chlorine is passed through a cold concentrated alkali solution, chloride and hypochlorite are formed (molecular chlorine is disproportionate to Cl +1 and Cl -1):
2KOH + Cl 2 → KCl + KClO + H 2 O
If chlorine is passed through a hot concentrated alkali solution, the molecular chlorine disproportionates into Cl +5 and Cl -1, resulting in the formation of chlorate and chloride, respectively:
3Cl 2 + 6KOH → 5KCl + KClO 3 + 3H 2 O
3) Chlorine, which has stronger oxidizing properties, is capable of oxidizing the sulfur contained in the acid salt:
Cl 2 + NaHS → NaCl + HCl + S↓
4) Acid salt - sodium hydrosulfide in an alkaline environment turns into sulfide:
2NaHS + 2KOH → K 2 S + Na 2 S + 2H 2 O
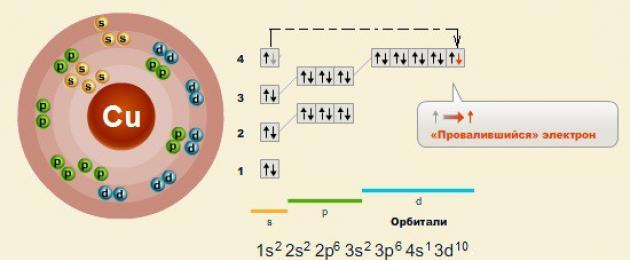
Like all d-elements, they are brightly colored.
Just like with copper it is observed electron failure- from s-orbital to d-orbital
Electronic structure of the atom:

Accordingly, there are 2 characteristic oxidation states of copper: +2 and +1.
Simple substance: golden-pink metal. 
Copper oxides:Сu2O copper (I) oxide \ copper oxide 1 - red-orange color
CuO copper (II) oxide \ copper oxide 2 - black.
Other copper compounds Cu(I), except the oxide, are unstable.
Copper compounds Cu(II) are, firstly, stable, and secondly, blue or greenish in color.
Why do copper coins turn green? Copper in the presence of water reacts with carbon dioxide air, CuCO3 is formed - a green substance.
Another colored copper compound, copper(II) sulfide, is a black precipitate.
Copper, unlike other elements, comes after hydrogen, and therefore does not release it from acids:
- With hot sulfuric acid: Cu + 2H2SO4 = CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O
- With cold sulfuric acid: Cu + H2SO4 = CuO + SO2 + H2O
- with concentrated:
Cu + 4HNO3 = Cu(NO3)2 + 4NO2 + 4H2O - with dilute nitric acid:
3Cu + 8HNO3 = 3 Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO +4 H2O
Example of the Unified State Examination C2 problem option 1:
Copper nitrate was calcined, and the resulting solid precipitate was dissolved in sulfuric acid. Hydrogen sulfide was passed through the solution, the resulting black precipitate was fired, and the solid residue was dissolved by heating in nitric acid.
2Сu(NO3)2 → 2CuO↓ +4 NO2 + O2
The solid precipitate is copper(II) oxide.
CuO + H2S → CuS↓ + H2O
Copper (II) sulfide is a black precipitate.
“Fired” means there was an interaction with oxygen. Not to be confused with "calcination". Calcinate - heat, naturally, at high temperature.
2СuS + 3O2 = 2CuO + 2SO2
The solid residue is CuO if the copper sulfide has reacted completely, CuO + CuS if it has reacted partially.
СuO + 2HNO3 = Cu(NO3)2 + H2O
CuS + 2HNO3 = Cu(NO3)2 + H2S
Another reaction is also possible:
СuS + 8HNO3 = Cu(NO3)2 + SO2 + 6NO2 + 4H2O
Example of the Unified State Examination C2 problem option 2:
Copper was dissolved in concentrated nitric acid, the resulting gas was mixed with oxygen and dissolved in water. Zinc oxide was dissolved in the resulting solution, then a large excess of sodium hydroxide solution was added to the solution.
As a result of the reaction with nitric acid, Cu(NO3)2, NO2 and O2 are formed.
NO2 was mixed with oxygen, which means it was oxidized: 2NO2 + 5O2 = 2N2O5. Mixed with water: N2O5 + H2O = 2HNO3.
ZnO + 2HNO3 = Zn(NO3)2 + 2H2O
Zn(NO 3) 2 + 4NaOH = Na 2 + 2NaNO 3
CuCl 2 + 4NH 3 = Cl 2
Na 2 + 4HCl = 2NaCl + CuCl 2 + 4H 2 O
2Cl + K 2 S = Cu 2 S + 2KCl + 4NH 3
When mixing solutions, hydrolysis occurs at both the weak base cation and the weak acid anion:
2CuSO 4 + Na 2 SO 3 + 2H 2 O = Cu 2 O + Na 2 SO 4 + 2H 2 SO 4
2CuSO 4 + 2Na 2 CO 3 + H 2 O = (CuOH) 2 CO 3 ↓ + 2Na 2 SO 4 + CO 2
Copper and copper compounds.
1) A constant electricity. The electrolysis product released at the cathode was dissolved in concentrated nitric acid. The resulting gas was collected and passed through a sodium hydroxide solution. The gaseous electrolysis product released at the anode was passed through a hot sodium hydroxide solution. Write the equations for the reactions described.
2) The substance obtained at the cathode during the electrolysis of molten copper (II) chloride reacts with sulfur. The resulting product was treated with concentrated nitric acid, and the liberated gas was passed through a solution of barium hydroxide. Write the equations for the reactions described.
3) The unknown salt is colorless and turns the flame yellow. When this salt is slightly heated with concentrated sulfuric acid, the liquid in which the copper dissolves is distilled off; the latter transformation is accompanied by the release of brown gas and the formation of a copper salt. During the thermal decomposition of both salts, one of the decomposition products is oxygen. Write the equations for the reactions described.
4) When a solution of salt A interacted with an alkali, a gelatinous, water-insoluble blue substance was obtained, which was dissolved in colorless liquid B to form a solution of blue color. The solid product remaining after careful evaporation of the solution was calcined; in this case, two gases were released, one of which is brown in color, and the second is part of the atmospheric air, and a black solid substance remains, which dissolves in liquid B to form substance A. Write the equations for the described reactions.
5) Copper turnings were dissolved in dilute nitric acid, and the solution was neutralized with caustic potash. The released blue substance was separated, calcined (the color of the substance changed to black), mixed with coke and calcined again. Write the equations for the reactions described.
6) Copper shavings were added to the solution of mercury (II) nitrate. After the reaction was completed, the solution was filtered, and the filtrate was added dropwise to a solution containing sodium hydroxide and ammonium hydroxide. In this case, a short-term formation of a precipitate was observed, which dissolved to form a bright blue solution. When an excess of sulfuric acid solution was added to the resulting solution, a color change occurred. Write the equations for the reactions described.
7) Copper (I) oxide was treated with concentrated nitric acid, the solution was carefully evaporated and the solid residue was calcined. The gaseous reaction products were passed through a large amount of water and magnesium shavings were added to the resulting solution, resulting in the release of a gas used in medicine. Write the equations for the reactions described.
8) The solid formed when malachite is heated was heated in a hydrogen atmosphere. The reaction product was treated with concentrated sulfuric acid and added to a solution of sodium chloride containing copper filings, resulting in the formation of a precipitate. Write the equations for the reactions described.
9) The salt obtained by dissolving copper in dilute nitric acid was subjected to electrolysis using graphite electrodes. The substance released at the anode was reacted with sodium, and the resulting reaction product was placed in a vessel with carbon dioxide. Write the equations for the reactions described.
10) The solid product of the thermal decomposition of malachite was dissolved by heating in concentrated nitric acid. The solution was carefully evaporated and the solid residue was calcined to give a black substance, which was heated in excess of ammonia (gas). Write the equations for the reactions described.
11) A solution of dilute sulfuric acid was added to the black powdery substance and heated. A solution of caustic soda was added to the resulting blue solution until the precipitation stopped. The precipitate was filtered and heated. The reaction product was heated in a hydrogen atmosphere, resulting in a red substance. Write the equations for the reactions described.
12) An unknown red substance was heated in chlorine, and the reaction product was dissolved in water. Alkali was added to the resulting solution, the resulting blue precipitate was filtered and calcined. When the calcination product, which is black in color, was heated with coke, a red starting material was obtained. Write the equations for the reactions described.
13) The solution obtained by reacting copper with concentrated nitric acid was evaporated and the precipitate was calcined. The gaseous products are completely absorbed by water, and hydrogen is passed over the solid residue. Write the equations for the reactions described.
14) Black powder, which was formed by burning a red metal in excess air, was dissolved in 10% sulfuric acid. Alkali was added to the resulting solution, and the resulting blue precipitate was separated and dissolved in an excess of ammonia solution. Write the equations for the reactions described.
15) A black substance was obtained by calcining the precipitate that is formed by the interaction of sodium hydroxide and copper (II) sulfate. When this substance is heated with coal, a red metal is obtained, which dissolves in concentrated sulfuric acid. Write the equations for the reactions described.
16) Copper metal was treated with iodine by heating. The resulting product was dissolved in concentrated sulfuric acid while heating. The resulting solution was treated with potassium hydroxide solution. The precipitate that formed was calcined. Write the equations for the reactions described.
17) Excess soda solution was added to copper (II) chloride solution. The precipitate that formed was calcined, and the resulting product was heated in a hydrogen atmosphere. The resulting powder was dissolved in dilute nitric acid. Write the equations for the reactions described.
18) Copper was dissolved in dilute nitric acid. An excess of ammonia solution was added to the resulting solution, observing first the formation of a precipitate, and then its complete dissolution with the formation of a dark blue solution. The resulting solution was treated with sulfuric acid until the characteristic blue color of copper salts appeared. Write the equations for the reactions described.
19) Copper was dissolved in concentrated nitric acid. An excess of ammonia solution was added to the resulting solution, observing first the formation of a precipitate, and then its complete dissolution with the formation of a dark blue solution. The resulting solution was treated with excess hydrochloric acid. Write the equations for the reactions described.
20) The gas obtained by reacting iron filings with a solution of hydrochloric acid was passed over heated copper (II) oxide until the metal was completely reduced. the resulting metal was dissolved in concentrated nitric acid. The resulting solution was subjected to electrolysis with inert electrodes. Write the equations for the reactions described.
21) Iodine was placed in a test tube with concentrated hot nitric acid. The released gas was passed through water in the presence of oxygen. Copper(II) hydroxide was added to the resulting solution. The resulting solution was evaporated and the dry solid residue was calcined. Write the equations for the reactions described.
22) Orange copper oxide was placed in concentrated sulfuric acid and heated. An excess of potassium hydroxide solution was added to the resulting blue solution. the resulting blue precipitate was filtered, dried and calcined. The resulting solid black substance was placed in a glass tube, heated, and ammonia was passed over it. Write the equations for the reactions described.
23) Copper (II) oxide was treated with a solution of sulfuric acid. During electrolysis of the resulting solution on an inert anode, gas is released. The gas was mixed with nitric oxide (IV) and absorbed with water. Magnesium was added to a dilute solution of the resulting acid, as a result of which two salts were formed in the solution, but no gaseous product was released. Write the equations for the reactions described.
24) Copper (II) oxide was heated in a stream of carbon monoxide. The resulting substance was burned in a chlorine atmosphere. The reaction product was dissolved in water. The resulting solution was divided into two parts. A solution of potassium iodide was added to one part, and a solution of silver nitrate was added to the second. In both cases, the formation of a precipitate was observed. Write the equations for the reactions described.
25) Copper(II) nitrate was calcined and the resulting solid was dissolved in dilute sulfuric acid. The solution of the resulting salt was subjected to electrolysis. The substance released at the cathode was dissolved in concentrated nitric acid. Dissolution proceeds with the release of brown gas. Write the equations for the reactions described.
26) Oxalic acid was heated with a small amount of concentrated sulfuric acid. The released gas was passed through a solution of calcium hydroxide. In which a precipitate fell. Some of the gas was not absorbed; it was passed over a black solid obtained by calcination of copper (II) nitrate. The result was a dark red solid. Write the equations for the reactions described.
27) Concentrated sulfuric acid reacted with copper. The gas released during the process was completely absorbed by an excess of potassium hydroxide solution. The copper oxidation product was mixed with the calculated amount of sodium hydroxide until precipitation stopped. The latter was dissolved in excess hydrochloric acid. Write the equations for the reactions described.
Copper. Copper compounds.
1. CuCl 2 Cu + Cl 2
at the cathode at the anode
2Cu(NO 3) 2 2CuO + 4NO 2 + O 2
6NaOH (hor.) + 3Cl 2 = NaClO 3 + 5NaCl + 3H 2 O
2. CuCl 2 Cu + Cl 2
at the cathode at the anode
CuS + 8HNO 3 (conc. horizon) = CuSO 4 + 8NO 2 + 4H 2 O
or CuS + 10HNO 3 (conc.) = Cu(NO 3) 2 + H 2 SO 4 + 8NO 2 + 4H 2 O
4NO 2 + 2Ba(OH) 2 = Ba(NO 3) 2 + Ba(NO 2) 2 + 2H 2 O
3. NaNO 3 (tv.) + H 2 SO 4 (conc.) = HNO 3 + NaHSO 4
Cu + 4HNO 3(conc.) = Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2NO 2 + 2H 2 O
2Cu(NO 3) 2 2CuO + 4NO 2 + O 2
2NaNO 3 2NaNO 2 + O 2
4. Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2NaOH = Cu(OH) 2 ↓ + 2NaNO 3
Cu(OH) 2 + 2HNO 3 = Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2H 2 O
2Cu(NO 3) 2 2CuO + 4NO 2 + O 2
CuO + 2HNO 3 = Cu(NO 3) 2 + H 2 O
5. 3Cu + 8HNO 3(diluted) = 3Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2NO + 4H 2 O
Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2KOH = Cu(OH) 2 ↓ + 2KNO 3
2Cu(NO 3) 2 2CuO + 4NO 2 + O 2
CuO + C Cu + CO
6. Hg(NO 3) 2 + Cu = Cu(NO 3) 2 + Hg
Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2NaOH = Cu(OH) 2 ↓ + 2NaNO 3
(OH) 2 + 5H 2 SO 4 = CuSO 4 + 4NH 4 HSO 4 + 2H 2 O
7. Cu 2 O + 6HNO 3 (conc.) = 2Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2NO 2 + 3H 2 O
2Cu(NO 3) 2 2CuO + 4NO 2 + O 2
4NO 2 + O 2 + 2H 2 O = 4HNO 3
10HNO3 + 4Mg = 4Mg(NO3)2 + N2O + 5H2O
8. (CuOH) 2 CO 3 2CuO + CO 2 + H 2 O
CuO + H2Cu + H2O
CuSO 4 + Cu + 2NaCl = 2CuCl↓ + Na 2 SO 4
9. 3Cu + 8HNO 3(diluted) = 3Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2NO + 4H 2 O
at the cathode at the anode
2Na + O 2 = Na 2 O 2
2Na 2 O 2 + CO 2 = 2Na 2 CO 3 + O 2
10. (CuOH) 2 CO 3 2CuO + CO 2 + H 2 O
CuO + 2HNO 3 Cu(NO 3) 2 + H 2 O
2Cu(NO 3) 2 2CuO + 4NO 2 + O 2
11. CuO + H 2 SO 4 CuSO 4 + H 2 O
CuSO 4 + 2NaOH = Cu(OH) 2 + Na 2 SO 4
Cu(OH) 2 CuO + H 2 O
CuO + H2Cu + H2O
12. Cu + Cl 2 CuCl 2
CuCl 2 + 2NaOH = Cu(OH) 2 ↓ + 2NaCl
Cu(OH) 2 CuO + H 2 O
CuO + C Cu + CO
13. Cu + 4HNO 3 (conc.) = Cu (NO 3) 2 + 2NO 2 + 2H 2 O
4NO 2 + O 2 + 2H 2 O = 4HNO 3
2Cu(NO 3) 2 2CuO + 4NO 2 + O 2
CuO + H2Cu + H2O
14. 2Cu + O 2 = 2CuO
CuSO 4 + NaOH = Cu(OH) 2 ↓ + Na 2 SO 4
Сu(OH) 2 + 4(NH 3 H 2 O) = (OH) 2 + 4H 2 O
15. CuSO 4 + 2NaOH = Cu(OH) 2 + Na 2 SO 4
Cu(OH) 2 CuO + H 2 O
CuO + C Cu + CO
Cu + 2H 2 SO 4 (conc.) = CuSO 4 + SO 2 + 2H 2 O
16) 2Cu + I 2 = 2CuI
2CuI + 4H 2 SO 4 2CuSO 4 + I 2 + 2SO 2 + 4H 2 O
Cu(OH) 2 CuO + H 2 O
17) 2CuCl 2 + 2Na 2 CO 3 + H 2 O = (CuOH) 2 CO 3 + CO 2 + 4NaCl
(CuOH) 2 CO 3 2CuO + CO 2 + H 2 O
CuO + H2Cu + H2O
3Cu + 8HNO 3(diluted) = 3Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2NO + 4H 2 O
18) 3Cu + 8HNO 3(diluted) = 3Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2NO + 4H 2 O
(OH) 2 + 3H 2 SO 4 = CuSO 4 + 2(NH 4) 2 SO 4 + 2H 2 O
19) Cu + 4HNO 3(conc.) = Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2NO + 2H 2 O
Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2NH 3 H 2 O = Cu(OH) 2 ↓ + 2NH 4 NO 3
Cu(OH) 2 + 4NH 3 H 2 O = (OH) 2 + 4H 2 O
(OH) 2 + 6HCl = CuCl 2 + 4NH 4 Cl + 2H 2 O
20) Fe + 2HCl = FeCl 2 + H 2
CuO + H 2 = Cu + H 2 O
Cu + 4HNO 3(conc.) = Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2NO 2 + 2H 2 O
2Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2H 2 O 2Cu + O 2 + 4HNO 3
21) I 2 + 10HNO 3 = 2HIO 3 + 10NO 2 + 4H 2 O
4NO 2 + 2H 2 O + O 2 = 4HNO 3
Cu(OH) 2 + 2HNO 3 Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2H 2 O
2Cu(NO 3) 2 2CuO + 4NO 2 + O 2
22) Cu 2 O + 3H 2 SO 4 = 2CuSO 4 + SO 2 + 3H 2 O
СuSO 4 + 2KOH = Cu(OH) 2 + K 2 SO 4
Cu(OH) 2 CuO + H 2 O
3CuO + 2NH 3 3Cu + N 2 + 3H 2 O
23) CuO + H 2 SO 4 = CuSO 4 + H 2 O
4NO 2 + O 2 + 2H 2 O = 4HNO 3
10HNO3 + 4Mg = 4Mg(NO3)2 + NH4NO3 + 3H2O
24) CuO + CO Cu + CO 2
Cu + Cl 2 = CuCl 2
2CuCl 2 + 2KI = 2CuCl↓ + I 2 + 2KCl
CuCl 2 + 2AgNO 3 = 2AgCl↓ + Cu(NO 3) 2
25) 2Cu(NO 3) 2 2CuO + 4NO 2 + O 2
CuO + H 2 SO 4 = CuSO 4 + H 2 O
2CuSO 4 + 2H 2 O 2Cu + O 2 + 2H 2 SO 4
Cu + 4HNO 3(conc.) = Cu(NO 3) 2 + 2NO 2 + 2H 2 O
26) H 2 C 2 O 4 CO + CO 2 + H 2 O
CO 2 + Ca(OH) 2 = CaCO 3 + H 2 O
2Cu(NO 3) 2 2CuO + 4NO 2 + O 2
CuO + CO Cu + CO 2
27) Cu + 2H 2 SO 4 (conc.) = CuSO 4 + SO 2 + 2H 2 O
SO 2 + 2KOH = K 2 SO 3 + H 2 O
СuSO 4 + 2NaOH = Cu(OH) 2 + Na 2 SO 4
Cu(OH) 2 + 2HCl CuCl 2 + 2H 2 O
Manganese. Manganese compounds.
I. Manganese.
In air, manganese is covered with an oxide film, which protects it from further oxidation even when heated, but in a finely crushed state (powder) it oxidizes quite easily. Manganese interacts with sulfur, halogens, nitrogen, phosphorus, carbon, silicon, boron, forming compounds with degree +2:
3Mn + 2P = Mn 3 P 2
3Mn + N 2 = Mn 3 N 2
Mn + Cl 2 = MnCl 2
2Mn + Si = Mn 2 Si
When reacting with oxygen, manganese forms manganese (IV) oxide:
Mn + O 2 = MnO 2
4Mn + 3O 2 = 2Mn 2 O 3
2Mn + O 2 = 2MnO
When heated, manganese reacts with water:
Mn+ 2H 2 O (steam) Mn(OH) 2 + H 2
In the electrochemical voltage series, manganese is located before hydrogen, therefore it easily dissolves in acids, forming manganese (II) salts:
Mn + H 2 SO 4 = MnSO 4 + H 2
Mn + 2HCl = MnCl 2 + H 2
Manganese reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid when heated:
Mn + 2H 2 SO 4 (conc.) MnSO 4 + SO 2 + 2H 2 O
With nitric acid under normal conditions:
Mn + 4HNO 3 (conc.) = Mn(NO 3) 2 + 2NO 2 + 2H 2 O
3Mn + 8HNO 3 (dil..) = 3Mn(NO 3) 2 + 2NO + 4H 2 O
Alkali solutions have practically no effect on manganese, but it reacts with alkaline melts of oxidizing agents, forming manganates (VI)
Mn + KClO 3 + 2KOH K 2 MnO 4 + KCl + H 2 O
Manganese can reduce the oxides of many metals.
3Mn + Fe 2 O 3 = 3MnO + 2Fe
5Mn + Nb 2 O 5 = 5MnO + 2Nb
II. Manganese compounds (II, IV, VII)
1) Oxides.
Manganese forms a number of oxides, the acid-base properties of which depend on the degree of oxidation of manganese.
Mn +2 O Mn +4 O2Mn2 +7 O 7
basic amphoteric acidic
Manganese(II) oxide
Manganese (II) oxide is obtained by reducing other manganese oxides with hydrogen or carbon monoxide (II):
MnO 2 + H 2 MnO + H 2 O
MnO 2 + CO MnO + CO 2
The main properties of manganese (II) oxide are manifested in their interaction with acids and acid oxides:
MnO + 2HCl = MnCl 2 + H 2 O
MnO + SiO 2 = MnSiO 3
MnO + N 2 O 5 = Mn(NO 3) 2
MnO + H 2 = Mn + H 2 O
3MnO + 2Al = 2Mn + Al 2 O 3
2MnO + O 2 = 2MnO 2
3MnO + 2KClO 3 + 6KOH = 3K 2 MnO 4 + 2KCl + 3H 2 O
- In contact with 0
- Google+ 0
- OK 0
- Facebook 0