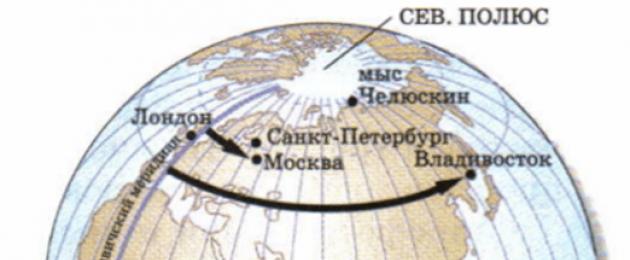
Video lesson “Geographical latitude and geographic longitude. Geographic Coordinates" will help you get an idea of geographic latitude and geographic longitude. The teacher will tell you how to correctly determine geographical coordinates.
Geographic latitude- arc length in degrees from the equator to a given point.
To determine the latitude of an object, you need to find the parallel on which this object is located.
For example, the latitude of Moscow is 55 degrees and 45 minutes north latitude, it is written like this: Moscow 55°45" N; latitude of New York - 40°43" N; Sydney - 33°52" S
Geographic longitude is determined by meridians. Longitude can be western (from the 0 meridian to the west to the 180 meridian) and eastern (from the 0 meridian to the east to the 180 meridian). Longitude values are measured in degrees and minutes. Geographic longitude can have values from 0 to 180 degrees.
Geographic longitude- length of the equatorial arc in degrees from the prime meridian (0 degrees) to the meridian of a given point.
The prime meridian is considered to be the Greenwich meridian (0 degrees).

Rice. 2. Determination of longitudes ()
To determine longitude, you need to find the meridian on which a given object is located.
For example, the longitude of Moscow is 37 degrees and 37 minutes east longitude, it is written like this: 37°37" east; the longitude of Mexico City is 99°08" west.

Rice. 3. Geographical latitude and geographic longitude
To accurately determine the location of an object on the surface of the Earth, you need to know its geographic latitude and geographic longitude.
Geographical coordinates- quantities that determine the position of a point on earth's surface using latitudes and longitudes.
For example, Moscow has the following geographic coordinates: 55°45"N and 37°37"E. The city of Beijing has the following coordinates: 39°56′ N. 116°24′ E First the latitude value is recorded.
Sometimes you need to find an object at already given coordinates; to do this, you must first guess in which hemispheres the object is located.
Homework
Paragraphs 12, 13.
1. What is geographic latitude and longitude?
Bibliography
Main
1. Basic course in geography: Textbook. for 6th grade. general education institutions / T.P. Gerasimova, N.P. Neklyukova. - 10th ed., stereotype. - M.: Bustard, 2010. - 176 p.
2. Geography. 6th grade: atlas. - 3rd ed., stereotype. - M.: Bustard, DIK, 2011. - 32 p.
3. Geography. 6th grade: atlas. - 4th ed., stereotype. - M.: Bustard, DIK, 2013. - 32 p.
4. Geography. 6th grade: cont. cards. - M.: DIK, Bustard, 2012. - 16 p.
Encyclopedias, dictionaries, reference books and statistical collections
1. Geography. Modern illustrated encyclopedia / A.P. Gorkin. - M.: Rosman-Press, 2006. - 624 p.
Literature for preparing for the State Exam and the Unified State Exam
1. Geography: initial course. Tests. Textbook manual for 6th grade students. - M.: Humanite. ed. VLADOS center, 2011. - 144 p.
2. Tests. Geography. 6-10 grades: Educational and methodological manual/ A.A. Letyagin. - M.: LLC "Agency "KRPA "Olympus": "Astrel", "AST", 2001. - 284 p.
Materials on the Internet
1. Federal Institute of Pedagogical Measurements ().
2. Russian Geographical Society ().
Latitude: 28°39′07″ N
Longitude: 77°13′53″E
Altitude: 227 m
Delhi coordinates in decimal degrees
Latitude: 28.6519500°
Longitude: 77.2314900°
Coordinates of Delhi in degrees and decimal minutes
Latitude: 28°39.117′N
Longitude: 77°13.8894′E
All coordinates are given in the WGS 84 world coordinate system.
WGS 84 is used in the GPS global positioning and navigation satellite system.
Coordinates (latitude and longitude) determine the position of a point on the Earth's surface. The coordinates are angular values. The canonical form of representing coordinates is degrees (°), minutes (′) and seconds (″). GPS systems widely use the representation of coordinates in degrees and decimal minutes or decimal degrees.
Latitude takes values from −90° to 90°. 0° - latitude of the equator; −90° - latitude of the South Pole; 90° - latitude of the North Pole. Positive values correspond to northern latitude (points north of the equator, abbreviated N or N); negative - southern latitude (points south of the equator, abbreviated as S or S).
Longitude is measured from the prime meridian (IERS Reference Meridian in the WGS 84 system) and takes values from −180° to 180°. Positive values correspond to east longitude (abbreviated as E or E); negative - western longitude (abbreviated as W or W).
Height above sea level shows the height of a point relative to conventional sea level. We use a digital elevation model
Delhi is one of the largest metropolises in Asia. This is an ancient and incredibly contrasting city, in which cramped old quarters coexist with new wide boulevards and spacious squares. In this article we will introduce you to New Delhi - one of its districts and, concurrently, the official capital of India.
Geography of the Indian capital: understanding toponyms
Before we begin our story, it is worth distinguishing between the concepts of “Delhi” and “New Delhi”. Delhi (officially the National Capital Territory of Delhi) is the center of the second largest metropolitan area in the country, home to at least 17 million people. The first settlement on the site of this huge metropolis arose in the 6th century BC.
What is New Delhi? De jure it is a separate city. In fact, it is only one of the districts of Delhi, located in its central part. The total area of New Delhi is 42.7 square meters. km. A number of other government institutions are also located here.
New Delhi means "New Delhi" in English. It is logical to assume that there must be Old Delhi somewhere. And it really does exist. Old city located north of New Delhi, closer to the banks of the Jamuna River. This is an incredibly dirty, noisy and, perhaps, the most colorful part of the metropolis.
Broadly speaking, the National Capital Territory of Delhi is divided into nine districts (see map below). With the exception of New Delhi, all other districts are named according to their geographical location on the city map: West, North, South, East, North-East, North-West, South-West, and Central Delhi.
Location and geographical coordinates of New Delhi
The city lies between the states of Haryana and Uttar Pradesh. Its territory is entirely located within the flat Indo-Gangetic Plain. Below you can see where New Delhi is located on a map of India.

On the eastern outskirts of the city flows the Jamuna River, the valley of which is extremely fertile.
The average height of the city above ocean level is 212 meters. New Delhi time zone: UTC+5:30 (used in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka). The time difference with Moscow is 2.5 hours.
A Brief History of "New Delhi"
The very name of the city speaks of its insignificant age. The official year of its foundation is 1911.
As you know, the capital of India since the end of the 16th century has been Calcutta. And Delhi, back in the Middle Ages, became an important financial center throughout South Asia. At the beginning of the twentieth century, the British government decided to move the capital from coastal Calcutta to Delhi, inland. This way, according to the British, it was easier to manage a huge colony.
At the end of 1911, George V solemnly laid the first stone of the future capital. Most New Delhi was planned by the famous architect Edwin Lutyens (1869-1944), in fact, the main architect British Empire interwar period. Built by him new town in India it was even nicknamed “Lachens' Delhi”.

New Delhi: climate and ecology
The city is located in a humid subtropical climate zone. Summers here are long and hot, and winters are short and moderately cold. The hottest months of the year are May and June (average air temperatures are 32.6° and 33.3°, respectively), the coldest is January (+13.8°).
The period from March to May is the least pleasant in terms of weather and climate. At this time, southwestern winds (the so-called “lu”) dominate, which bring dryness, incredible heat and a lot of sand to the city. In mid-June, the situation is slightly softened by wet and cool monsoons blowing from the northeast. In November, climatic winter begins here, which is accompanied by dense fogs. However, air temperatures very rarely drop below +10 degrees.
According to WHO (World Health Organization), the level of air pollution in New Delhi is 90 times higher than all permissible standards. The head of the city once even compared the capital to a “gas chamber.” What causes such an unfavorable environmental situation? There are actually several reasons. Firstly, the air is heavily polluted by the coal-fired power plant in Badarpur. Secondly, local residents actively burn garbage and plant remains from their gardens in the city. All this leads to high smoke levels in the atmosphere.

Population and economy
The population of New Delhi is about 300 thousand people, which is approximately one fiftieth of the total number of residents of the Delhi metropolis. There are only 821 women per 1,000 men in the city. Residents mainly profess Hinduism. The capital also has adherents of Islam (11%), Sikhism (about 4%) and Christianity (no more than 1%).
The main language used in the city, both spoken and writing- this is Hindi. Urdu and Punjabi are also used, as well as languages of other linguistic groups of India (Telugu, Marathi, Maithili and others). English is spoken quite often in New Delhi.
The modern capital of India is also one of the main financial, cultural and scientific centers of the country. services) occupies a leading place in the structure of the city economy. It accounts for at least 78% of New Delhi's GDP. The main employer in the Indian capital is the government sector. The city has very developed banking and information technologies, hotel and tourism business.
Urban transport
Transport in the capital is represented by the metro, suburban railways, taxis, buses and autorickshaws. The fastest and most convenient way to get around the city is the metro. It is cool here and there are no traffic jams, which so often plague the streets of the capital. Four (out of six) lines of the capital's metro pass directly through New Delhi.

Buses are cheaper transport than the metro. Therefore, it is the most popular in the city, providing up to 60% of passenger traffic. It is important to know that in Delhi there are two types of buses - public (red or green) and private. On hot days, it is better to use the latter, since their interiors have air conditioning.
One taxi trip to New Delhi costs approximately 250-300 Russian rubles. Auto-rickshaws are also popular in the city. They move slower than taxis, but with the breeze.
Planning features and urban architecture
New Delhi embodies the imperial traditions of interwar Britain. The heart of the city is the Presidential Palace, located on a hilltop. In close proximity to it is Parliament and the Anglican Cathedral. The park-like Rajpath Marj connects the President's Palace with the Public Garden and India Gate. It is these two buildings that dominate the planning structure of New Delhi.
The city was built according to the design of Edwin Lutyens. He also designed the key buildings of the ensemble - the Capitol, the Presidential Palace, the Cannot Place shopping center, as well as residences for numerous English nobility. The main goal that stood before the architect was to create a kind of “British Rome” in India - majestic and monumental. And the architect coped with this task.

During the construction of the city, for the first time in India, a radial-ring layout of streets and squares was used. An important feature of the Indian capital is the presence of vast expanses of parks and gardens. In total, they occupy about 40% of the entire area of New Delhi. In the development of the capital, the ensemble of government buildings - the Capitol - stands out spectacularly. In its pomp, it is very reminiscent of similar architectural ensembles in Canberra or Washington.
Delhi is one of the largest metropolises in Asia. This is an ancient and incredibly contrasting city, in which cramped old quarters coexist with new wide boulevards and spacious squares. In this article we will introduce you to New Delhi - one of its districts and, concurrently, the official capital of India.
Geography of the Indian capital: understanding toponyms
Before we begin our story, it is worth distinguishing between the concepts of “Delhi” and “New Delhi”. Delhi (officially the National Capital Territory of Delhi) is the center of the second largest metropolitan area in the country, home to at least 17 million people. The first settlement on the site of this huge metropolis arose in the 6th century BC.
What is New Delhi? De jure it is a separate city. In fact, it is only one of the districts of Delhi, located in its central part. The total area of New Delhi is 42.7 square meters. km. The Government of India and a number of other government agencies are located here.
New Delhi means "New Delhi" in English. It is logical to assume that there must be Old Delhi somewhere. And it really does exist. The old city is located north of New Delhi, closer to the banks of the Jamuna River. This is an incredibly dirty, noisy and, perhaps, the most colorful part of the metropolis.
Broadly speaking, the National Capital Territory of Delhi is divided into nine districts (see map below). With the exception of New Delhi, all other districts are named according to their geographical location on the city map: West, North, South, East, North-East, North-West, South-West, and Central Delhi.
Location and geographical coordinates of New Delhi
The city is located in North India, between the states of Haryana and Uttar Pradesh. Its territory is entirely located within the flat Indo-Gangetic Plain. Below you can see where New Delhi is located on a map of India.

On the eastern outskirts of the city flows the Jamuna River, the valley of which is extremely fertile.
The average height of the city above ocean level is 212 meters. New Delhi time zone: UTC+5:30 (used in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka). The time difference with Moscow is 2.5 hours.
A Brief History of "New Delhi"
The very name of the city speaks of its insignificant age. The official year of its foundation is 1911.
As you know, the capital of India since the end of the 16th century has been Calcutta. And Delhi, back in the Middle Ages, became an important financial center throughout South Asia. At the beginning of the twentieth century, the British government decided to move the capital from coastal Calcutta to Delhi, inland. This way, according to the British, it was easier to manage a huge colony.
At the end of 1911, George V solemnly laid the first stone of the future capital. Much of New Delhi was planned by the famous architect Edwin Lutyens (1869-1944), essentially the chief architect of the British Empire during the interwar period. The new city he built in India was even nicknamed “Lachens' Delhi.”
New Delhi: climate and ecology
The city is located in a humid subtropical climate zone. Summers here are long and hot, and winters are short and moderately cold. The hottest months of the year are May and June (average air temperatures are 32.6° and 33.3°, respectively), the coldest is January (+13.8°).
The period from March to May is the least pleasant in terms of weather and climate. At this time, southwestern winds (the so-called “lu”) dominate, which bring dryness, incredible heat and a lot of sand to the city. In mid-June, the situation is slightly softened by wet and cool monsoons blowing from the northeast. In November, climatic winter begins here, which is accompanied by dense fogs. However, air temperatures very rarely drop below +10 degrees.
According to WHO (World Health Organization), the level of air pollution in New Delhi is 90 times higher than all permissible standards. The head of the city once even compared the capital to a “gas chamber.” What causes such an unfavorable environmental situation? There are actually several reasons. Firstly, the air is heavily polluted by the coal-fired power plant in Badarpur. Secondly, local residents actively burn garbage and plant remains from their gardens in the city. All this leads to high smoke levels in the atmosphere.

Population and economy
The population of New Delhi is about 300 thousand people, which is approximately one fiftieth of the total number of residents of the Delhi metropolis. There are only 821 women per 1,000 men in the city. Residents mainly profess Hinduism. The capital also has adherents of Islam (11%), Sikhism (about 4%) and Christianity (no more than 1%).
The main language used in the city, both spoken and written, is Hindi. Urdu and Punjabi are also used, as well as languages of other linguistic groups of India (Telugu, Marathi, Maithili and others). English is spoken quite often in New Delhi.
The modern capital of India is also one of the main financial, cultural and scientific centers of the country. Tertiary sector (sphere services) occupies a leading place in the structure of the city economy. It accounts for at least 78% of New Delhi's GDP. The main employer in the Indian capital is the government sector. The city has very developed banking, information technology, hotel and tourism businesses.
Urban transport
Transport in the capital is represented by the metro, suburban railways, taxis, buses and autorickshaws. The fastest and most convenient way to get around the city is the metro. It is cool here and there are no traffic jams, which so often plague the streets of the capital. Four (out of six) lines of the capital's metro pass directly through New Delhi.

Buses are cheaper transport than the metro. Therefore, it is the most popular in the city, providing up to 60% of passenger traffic. It is important to know that in Delhi there are two types of buses - public (red or green) and private. On hot days, it is better to use the latter, since their interiors have air conditioning.
One taxi trip to New Delhi costs approximately 250-300 Russian rubles. Auto-rickshaws are also popular in the city. They move slower than taxis, but with the breeze.
Planning features and urban architecture
New Delhi embodies the imperial traditions of interwar Britain. The heart of the city is the Presidential Palace, located on a hilltop. In close proximity to it is Parliament and the Anglican Cathedral. The park-like Rajpath Marj connects the President's Palace with the Public Garden and India Gate. It is these two buildings that dominate the planning structure of New Delhi.
The city was built according to the design of Edwin Lutyens. He also designed the key buildings of the ensemble - the Capitol, the Presidential Palace, the Cannot Place shopping center, as well as residences for numerous English nobility. The main goal that stood before the architect was to create a kind of “British Rome” in India - majestic and monumental. And the architect coped with this task.

During the construction of the city, for the first time in India, a radial-ring layout of streets and squares was used. An important feature of the Indian capital is the presence of vast expanses of parks and gardens. In total, they occupy about 40% of the entire area of New Delhi. In the development of the capital, the ensemble of government buildings - the Capitol - stands out spectacularly. In its pomp, it is very reminiscent of similar architectural ensembles in Canberra or Washington.
- In contact with 0
- Google+ 0
- OK 0
- Facebook 0