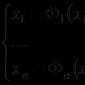FRACTION (in arithmetic) FRACTION (in arithmetic)
FRACTION, in arithmetic - a number made up of a whole number of fractions of one. A fraction is expressed as the ratio of two integers m/n, where n- denominator of a fraction - shows how many parts the unit is divided into, and m- the numerator of the fraction - shows how many such shares are contained in the fraction. If the numerator of the fraction is less than the denominator, then the fraction is called correct (eg, 5/7), if it is greater than or equal, it is called improper (eg, 7/4). A fraction whose denominator is a power of 10 (eg 10, 100, 1000, etc.) is called a decimal; to record it, write out from left to right the number of whole units, and then, after the decimal point, tenths, hundredths, etc., of fractions. (e.g. 245/100 = 2.45).
encyclopedic Dictionary. 2009 .
- DROBYSHEVA Nina Ivanovna
- SHOT (gunshot)
See what "FRACTION (in arithmetic)" is in other dictionaries:
Fraction (in arithmetic)- A fraction in arithmetic, a number made up of a whole number of fractions of one. D. is depicted by the symbol where m is the numerator of D. - shows the number of shares of the unit taken, divided into as many shares as the denominator n shows (marks). D. can ... ...
FRACTION- in arithmetic, a number made up of a whole number of fractions of one. A fraction is expressed as the ratio of two integers m / n, where n the denominator of the fraction shows how many shares the unit is divided into, and m the numerator of the fraction shows how many such shares ... ... Big Encyclopedic Dictionary
fraction- and; and. 1. collected. Small lead balls for shooting from a hunting rifle. Load the shotgun. Shoot small shot. Put shot in the gun. 2. collected Frequent, rhythmically repeated sounds from blows to something l. D. rain, hail. Heard…… encyclopedic Dictionary
Fraction (mathematics)- This term has other meanings, see Fraction. 8 / 13 numerator numerator denominator denominator Two entries of one fraction A fraction in mathematics is a number consisting of one or more parts ... ... Wikipedia
Fraction- I in arithmetic, a number made up of a whole number of fractions of one. D. is depicted by the symbol where m is the numerator D. shows the number of shares of the unit taken, divided into as many shares as it shows (marks) ... ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
FRACTION- in arithmetic, a number made up of a whole number of fractions of one. D. is expressed by the ratio of two integers m / n, where n the denominator D. shows how many shares the unit is divided, and t the numerator D. shows how many such shares are contained in D. ... ... Natural science. encyclopedic Dictionary
Periodic fraction- an infinite decimal fraction, in which, starting from a certain place, there is only a periodically repeating certain group of digits. For example, 1.3181818...; in short, this fraction is written like this: 1.3 (18), that is, they put the period in brackets (and ... ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
We use fractions all the time in our lives. For example, when we eat cake with friends. The cake can be divided into 8 equal parts or 8 shares. share is an equal part of something whole. Four friends each ate a piece of cake. Four picked out of eight pieces can be written mathematically as common fraction\(\frac(4)(8)\), the fraction reads “four-eighths” or “four divided by eight”. Common fraction is also called simple fraction.
The fractional bar replaces division:
\(4 \div 8 = \frac(4)(8)\)
We wrote down the shares in fractions. In literal form it will be like this:
\(\bf m \div n = \frac(m)(n)\)
4 – numerator or divisible, is above the fractional bar and shows how many parts or shares from the total were taken.
8 – denominator or divisor, located below the fractional bar and shows the total number of parts or shares.
If we look closely, we will see that the friends ate half of the cake, or one part out of two. We write in the form of an ordinary fraction \(\frac(1)(2)\), it reads “one second”.

Consider another example:
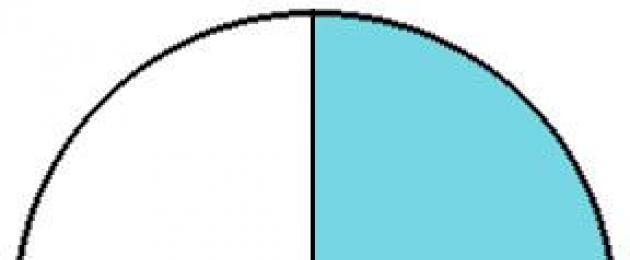
There is a square. The square is divided into 5 equal parts. Painted two parts. Write a fraction for the shaded parts? Write down the fraction for the unshaded parts?

Two parts are painted over, and there are five parts in total, so the fraction will look like \(\frac(2)(5)\), the fraction “two-fifths” is read.
Three parts were not painted over, there are five parts in total, so we write the fraction like this \(\frac(3)(5)\), the fraction “three-fifths” is read.
Divide the square into smaller squares and write fractions for the shaded and unshaded parts. 
Shaded 6 parts, and only 25 parts. We get the fraction \(\frac(6)(25)\) , the fraction “six twenty-fifths” is read.
Not shaded 19 parts, but only 25 parts. We get the fraction \(\frac(19)(25)\), the fraction “nineteen twenty-fifths” is read.

Shaded 4 parts, and only 25 parts. We get the fraction \(\frac(4)(25)\), the fraction “four twenty-fifths” is read.
Not shaded 21 parts, but only 25 parts. We get the fraction \(\frac(21)(25)\), the fraction “twenty-one twenty-fifths” is read.
Any natural number can be expressed as a fraction. For example:
\(5 = \frac(5)(1)\)
\(\bf m = \frac(m)(1)\)
Any number is divisible by one, so this number can be represented as a fraction.
Questions on the topic “ordinary fractions”:
What is a share?
Answer: share is an equal part of something whole.
What does the denominator show?
Answer: the denominator shows how many parts or shares are divided.
What does the numerator show?
Answer: The numerator shows how many parts or shares were taken.
The road was 100m. Misha walked 31m. Write down the expression as a fraction, how long did Misha go?
Answer:\(\frac(31)(100)\)
What is a common fraction?
Answer: A common fraction is the ratio of the numerator to the denominator, where the numerator is less than the denominator. Example, common fractions \(\frac(1)(4), \frac(3)(7), \frac(5)(13), \frac(9)(11)…\)
How to convert a natural number to a common fraction?
Answer: any number can be written as a fraction, for example, \(5 = \frac(5)(1)\)
Task #1:
Bought 2kg 700g of melon. Misha's \(\frac(2)(9)\) melons were cut off. What is the mass of the cut piece? How many grams of melon are left?
Solution:
Convert kilograms to grams.
2kg = 2000g
2000g + 700g = 2700g total melon weighs.
Misha's \(\frac(2)(9)\) melons were cut off. The denominator is 9, which means the melon was divided into 9 parts.
2700: 9 = 300g weight of one piece.
The numerator is the number 2, so Misha needs to give two pieces.
300 + 300 = 600g or 300 ⋅ 2 = 600g is how many melons Misha ate.
To find what mass of melon is left, you need to subtract the mass eaten from the total mass of melon.
2700 - 600 = 2100g melons left.
§ 115. Shares of a unit. We have already met with such units of measurement that can be divided into equal parts. So, 1 m can be divided into 100 cm; one day can be divided into 24 hours.
We call a centimeter a hundredth of a meter; just like we call the hour twenty fourth part of the day. A millimeter is a thousandth of a meter. A day is three hundred and sixty-fifth of a simple (i.e., non-leap) year. In all these cases, instead of "part" they sometimes say "share" (this word is more convenient, because the word "part" has a different meaning in our language). Thus, a gram is a thousandth of a kilogram, a minute is a sixtieth of an hour.
The second beat is called half, third beat third, fourth beat quarter.
§ 116. Fractional number. One fraction or a collection of several identical fractions of a unit is called a fraction.
For example: 1 tenth, 3 fifths, 12 sevenths are fractions.
An integer together with a fraction makes a mixed number; for example, 3 whole 7 eighths (i.e. 3 whole units, to which 7 eighths of a unit are added).
Fractions and mixed numbers are called fractional numbers, in contrast to integers made up of whole units.
§ 117. Image of a fraction. It is customary to represent a fraction like this: they write a number showing how many parts are contained in the fraction; draw a line under it; under the line put another number showing how many equal parts the unit is divided into, from which the fraction is taken. For example, 3 fifths are depicted as follows:.
The number above the line is called numerator fractions; it shows the number of parts that make up a fraction. The number below the line is called denominator fractions; it shows how many equal parts the unit has been divided. Both of these numbers together are called fraction members.
A mixed number is depicted as follows: they write an integer and, on the right side, a fraction is attributed to it; for example, the number 3 and two sevenths are depicted as follows:.
§ 118. Obtaining fractional numbers when measuring. Suppose we want to measure some length with a meter. Assume that a meter in this length fits 7 times, and the remainder is less than a meter. In order to measure this remainder, we look for such a fraction of a meter that, if possible, would fit into the remainder without a new remainder. Let it turn out that the tenth of a meter fits into the remainder exactly 3 times. Then we say that the measured length is equal to a meter.
Similarly, fractional numbers can be obtained by measuring weight (for example, a gram), when measuring time (for example, an hour), etc.
So a fractional number can appear as measurement result.
§ 119. Obtaining fractional numbers when dividing an integer into equal parts. Let it be required to divide 5 kg of bread into 8 equal parts. We can make this division like this; imagine that each kilogram of bread is divided into 8 equal parts (into eighths); then in 5 kg of bread there will be 8 · 5 such shares, i.e. 40, and in one eighth of 5 kg of bread there should be 40: 8, i.e. 5. This means that an eighth of 5 kg is equal to one kilogram (and in general an eighth of 5 of some units is equal to one such unit).
Let's take another example: it is required to reduce the number 28 by 5 times, i.e., instead of 28, it is required to take one fifth of this number. 28 is the sum of the numbers 25 and 3. The fifth part of the number 25 is 5. To find the fifth of 3, we divide each unit into 5 equal parts; taking from each unit by , we find that the fifth of three units will be . So the fifth part of the number 28 is .
But you can also find the fifth part of the number 28 like this: the fifth part of one unit is; a fifth of another unit is also ; if, thus, we take a fifth of each of the 28 units, then we get. Thus: to divide an integer into several equal parts, it is enough to take this integer as the numerator of a fraction, and write another number as the denominator, showing how many equal parts the integer is divided into.
Examples. One twelfth of the number 7 is ; a quarter of the number 15 is ; the fraction is the thirteenth part of the number 8; The fraction is one sixth of the number 29.
Consequence. Any fraction can be considered not only as a collection of several equal parts of a unit, but also as one fraction of several whole units. So, a fraction is not only 5 eighths of one unit, but also one eighth of 5 units.
§ 120. Equality and inequality of fractional numbers. Two fractional numbers are considered equal if the values expressed by these numbers are equal to each other.
Let's take some fraction, for example (let it be the length shown in Fig. 2). Divide each quarter in half. We will then get smaller shares; in one quarter of such shares 2; it means that there are 2 4 = 8 of them in the unit; hence it is eighths; three-quarters of these eighths contains 2 3 = 6; so the fraction is equal to the fraction; by this we mean that two lengths of which one is a meter and the other a meter are equal to each other; or that two weights, of which one is equal to a kilogram and the other to a kilogram, are equal to each other, etc.
Of two unequal fractional numbers, the larger one is considered to be the one that expresses a larger value. with the same unit of measure. So, if we say that, we want to express by this that, for example, a gram is more than a gram, an hour is more than an hour, etc.
If two fractions have the same numerators, then the larger one will be the one with less denominator, because it contains the same number of larger fractions of unity than the other. Yes, more than .
§ 121. The fraction is correct and incorrect. A fraction whose numerator is less than the denominator is called proper: a fraction whose numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator is called irregular. Obviously, the correct fraction is less than one, and the incorrect one is greater than or equal to it; for example:
§ 122. Converting an integer to an improper fraction. Any whole number can be expressed in any number of fractions of one. Let, for example, it is required to express 8 in twentieth shares. There are 20 twentieths in one unit; therefore, in 8 units there will be 20 8, i.e. 160. So
Similarly, the number 25 will be expressed in fourths, the number 100 will be expressed in seventeenths, etc.
Rule. To express an integer as an improper fraction with a given denominator, you need to multiply this denominator by a given number and take the resulting product as the numerator, and write the denominator given.
Remark . An integer is sometimes useful to represent as such a fraction, in which the numerator is equal to this hollow number, and the denominator is one. So, instead of 5 they sometimes write (the first five). To give meaning to such expressions, it is agreed that the "first" part of a number is the number itself.
§ 123. Conversion of a mixed number to an improper fraction. Suppose you want to convert a mixed number to an improper fraction. This means to find out how many fifths are in eight whole units, together with three fifths of the same unit. One unit contains 5 fifths; therefore, in eight units there will be 5 8 of them, i.e. 40; this means that in eight units, together with three-fifths of such shares, there will be 40 + 3, i.e. 43.
So, . Like this:
Rule. In order to turn the mixed number into an improper fraction, the integer is multiplied by the denominator, the numerator is added to the resulting product and this amount is taken as the numerator of the required fraction, and the denominator is left the same.
§ 124. Conversion of an improper fraction to a mixed number. Let it be required to convert an improper fraction into a mixed number, that is, to find out how many whole units are in this improper fraction and how many eighths that do not make up one. Since the unit contains 8 eighths, then 100 eighths contain as many units as 8 eighths are contained in 100 eighths. 8 eighths in 100 eighths are contained 12 times, with 4 eighths remaining. So 100 eighths contains 12 whole ones and 4 more eighths. So,
Rule. To convert an improper fraction to a mixed or whole number, divide the numerator by the denominator; the integer quotient from this division will show how many whole units, and the remainder, how many more fractions of one in the mixed number.
The conversion of an improper fraction to a mixed number is sometimes also called the elimination of a whole number from this fraction.
- In contact with 0
- Google Plus 0
- OK 0
- Facebook 0