1)
C6H6
2)
C5H8
3)
C6H14
4)
C6H12
2. The C≡C bond length and the bond angle in alkyne molecules, respectively, are
1)
180˚ and 0.154 nm
3)
120˚ and 0.134 nm
2)
180˚ and 0.120 nm
4)
109˚28′ and 0.154 nm
3. KMnO4 solution decolorizes both substances in the series
1)
propine and propane
3)
acetylene and ethylene
2)
butadiene-1,3 and butane
4)
butylene and isobutane
4. As a result of the Kucherov reaction,
1)
ethanol
2)
ethane
3)
ethanal
4)
ethanediol-1,2
5. Acetylene is produced in industry using
1)
hydrolysis of calcium carbide
3)
oil distillation
2)
methane pyrolysis
4)
ethene hydrogenation
6. Ethine can be distinguished from ethane by
1)
litmus
3)
copper(II) hydroxide
2)
aqueous solution of alkali
4)
bromine water
7. Which of the following statements about propyne and its properties are correct?
A. The propyne molecule contains a tetrahedral fragment of atoms.
B. Propyne can be distinguished from propane using an aqueous solution of potassium permanganate.
1)
only A is correct
2)
only B is correct
3)
both statements are true
4)
both statements are wrong
8. In the scheme of transformations
CaC2 X1 X2
substances X1 and X2 are respectively
1)
C2H4 and C2H5Cl
3)
C2H2 and CH2Cl-CH2Cl
2)
C2H2 and CH2=CHCl
4)
CH4 and CH3Cl
9. Propyne is able to react with each of the substances indicated in the row
1)
KOH, C6H6, Br2
4)
H2, O2, Na
2)
Cu, H2, H2O
5)
KMnO4, CH4, HBr
3)
Cl2, HCl, OH
6)
H2O, Cl, Cl2
B. CH3 - C \u003d CH.
D. CH3 - C \u003d C - CH2 - CH3.
2. The first member of the homologous series of alkynes:
B. Propin.
3. Pentin-1 isomer is:
A. Penten-1.
B. 2-Methylbutane.
B. 3-Methylbutin-1.
D. 3-Methylpentine-1.
4. The bond between carbon atoms in the acetylene molecule:
A. Single.
B. Triple.
B. Double.
G. One and a half.
5. The formula of the substance, which is characterized by the hydrogenation reaction:
6. Method for obtaining butyne-1.
A. Dehydrogenation of butene-1.
B. Chlorination of methane.
B. Dehydrogenation of propane.
D. Hydration of butene-1.
7. Raw materials for the industrial production of polyvinyl chloride:
A. Acetylene. B. Chloroethane.
B. Ethylene. G. Butadiene-1,3.
8. Bromine water becomes colorless when a substance is passed through it, the formula of which is:
D. C4H10. 9. Catalyst in the Kucherov reaction:
A. Sulfuric acid.
B. Aluminum chloride.
B. Mercury sulfate (II).
G. Platinum.
10. The formula of a hydrocarbon, upon complete combustion of 1 mol of which 4 mol of carbon monoxide (IV) and 3 mol of water are formed: A. С4Н8. B. C4H10. B. C2H6. D. C4H6. Part B. Free Answer Tasks
11. What are the colors and markings of steel cylinders used to store methane and acetylene?
12. Derive the formula of a hydrocarbon, 2.24l of which (n.o.) has a mass of 4g.
13. Make the reaction equations according to the given scheme: calcium carbonate => calcium carbide => acetylene. Specify the conditions for their implementation.
1. Know the general formula of alkanes, formulas and names of substances of the homologous series of alkanes (up to octane);2. Know the definitions: homologues, homologous series, isomers, isomerism. Be able to write formulas of isomers, determine the type of isomerism.
Write isomer formulas for C4H10 and for C4H8.
3. Know the chemical properties of alkanes, be able to write reaction equations.
4. Know the general formula of alkenes, formulas and names of substances of the homologous series of alkenes (up to octene)
5. Know the chemical properties of alkenes, be able to write reaction equations
6. Application of alkanes and alkenes
7. Know the general formula of alkynes and alkadienes (up to C7)
8. Know the chemical properties of alkynes, be able to write reaction equations.
9. Know the general formula of benzene, its chemical properties, application
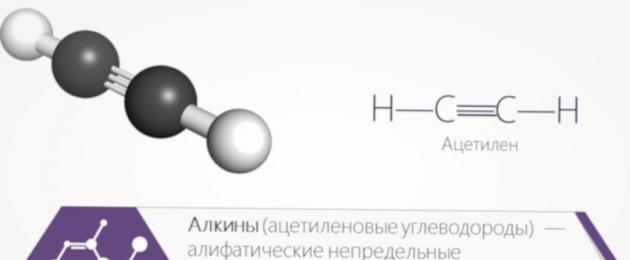
Alkynes (otherwise acetylenic hydrocarbons) are hydrocarbons containing a triple bond between carbon atoms, with the general formula CnH2n-2. The carbon atoms in the triple bond are in a state of sp - hybridization.
Reaction of acetylene with bromine water
The acetylene molecule contains a triple bond, bromine destroys it and joins the acetylene. Terabromomethane is formed. Bromine is consumed in the formation of tetrabromoethane. Bromine water (yellow) - discolors.
This reaction proceeds at a lower rate than in the series of ethylene hydrocarbons. The reaction also proceeds in steps:
HC ≡ CH + Br 2 → CHBr = CHBr + Br 2 → CHBr 2 - CHBr 2
acetylene → 1,2-dibromoethane → 1,1,2,2-tetrabromoethane
The decolorization of bromine water proves the unsaturation of acetylene.
The reaction of acetylene with a solution of potassium permanganate
In a solution of potassium permanganate, acetylene is oxidized, and the molecule breaks at the site of the triple bond, the solution quickly becomes colorless.
3HC ≡ CH + 10KMnO 4 + 2H 2 O → 6CO 2 + 10KOH + 10MnO 2
This reaction is a qualitative reaction for double and triple bonds.
The reaction of acetylene with an ammonia solution of silver oxide
If acetylene is passed through an ammonia solution of silver oxide, the hydrogen atoms in the acetylene molecule are easily replaced by metals, since they have high mobility. In this experiment, hydrogen atoms are replaced by silver atoms. Silver acetylenide is formed - a yellow precipitate (explosive).
CH ≡ CH + OH → AgC≡CAg↓ + NH 3 + H 2 O
This reaction is a qualitative reaction for a triple bond.
Bromine and bromine water are used in medicine, construction, agriculture and many other areas of human life.
Bromine water is a yellow-orange liquid, however, it becomes colorless during some reactions. Why is this happening? And what substances can affect the change in its color?
Bromine water is an aqueous solution of bromine. It is able to oxidize metals, as well as a number of organic compounds. When reacting with compounds containing multiple bonds, it becomes colorless. This process is a qualitative reaction to the unsaturation of organic compounds. The disappearance of the color of the solution is evidence of unsaturation.
Examples of bromine water decolorization reactions
When bromine water reacts with alkynes and alkenes, the resulting solution becomes colorless. Alkenes have an unsaturated double bond, and alkynes have a triple bond, which determines their properties. During the interaction, double and triple bonds are broken, bromine is added. As a result, bromine compounds are formed. Alkanes do not decolorize bromine water.

An aqueous solution of bromine also loses color when interacting with unsaturated oils, which also have double and triple bonds.
During the reaction of potassium iodide and an aqueous solution of bromine, free iodine molecules are removed, and the solution becomes discolored.
In order to be convinced of the given examples, a simple mixing of these substances in laboratory conditions is sufficient. Heating, exposure to light, participation of catalysts is not required. Such experiments are carried out while studying at school and vocational education institutions, but they should not be carried out at home, since bromine is toxic and has a strong unpleasant odor.
3) CH3 O CH3
4) CH3COO CH3
3. Specify the compound containing the carboxyl group:
1) aromatic alcohol
2) aldehyde
3) simple ether
4. Specify the compound containing the carbonyl group:
1) aromatic alcohol
2) aldehyde
3) simple ether
4) unsaturated polybasic acid
5.Give a name to the connection: O
CH3 - CH - CH - C
1) 2-methyl-3-bromobutanol-1
2) 2-bromo-3-methylbutanal
3) 2-methyl-3-bromobutanal
4) 2-bromo-3-methylpropanal
6. Reaction CH3CHO+Ag2O CH3COOH+2 Ag:
1) Polycondensation
2) Esterification
3) "silver mirror"
4) Kucherova
7. The functional group of carboxylic acids is called:
1) Carbonyl
2) Hydroxyl
3) Carboxyl
4) ester
8. Acetic acid does not react with the following metal:
9. What is the name of the aldehyde:
1) 2-Methyl-3-propylbutanal;
2) 2,3-dimethylhexanal;
3) 4,5-dimethylhexanal;
4) 2-methyl-2-propylbutanal
10. Specify the general formula of carbohydrates:
11. Indicate the carbohydrate that is the main part of wood:
1) Starch
2) Cellulose
4) Maltose
12. Specify the formula of fructose:
13. Pentose, which is part of DNA, is:
1) Glucose
2) Fructose
4) Deoxyribose
14. Milk sugar is a disaccharide:
1) Sucrose
2) Maltose
3) Lactose
4) Galactose
15. Beet or cane sugar is a disaccharide:
1) Maltose
2) Sucrose
3) Galactose
4) Lactose
16. Malt Sugar:
1) Galactose
2) Sucrose
3) Lactose
4) Maltose
17. In plant cells, starch performs the following function:
1) Transfer of hereditary information
2) Supply of nutrients
3) Construction and structural
4) Catalyst for biological processes
18. In plant cells, cellulose performs the following function:
1) Supply of nutrients
2) Catalyst of biological processes
3) Construction and structural
4) Transfer of hereditary information
19. Give a name to the connection:
CH3 - CH - CH - CH3
1) 3-methylbutanol-2 3) 3-methylpropanone-2
2) 2-methylbutanol-3 4) 2-methylpropanal-2
20. Write the equation for a chemical reaction and give it a name:
R1 - C + HO - R2 ↔
1) hydration 3) attachment
2) esterification reaction 4) substitution
Among the characteristics listed below, select those that, as a rule, relate to liquid fats - oils:
1) They are of plant origin
2) They are of animal origin
3) Highly soluble in water
4) Highly soluble in organic solvents
7) Discolor bromine water
8) Are esters of glycerol
Give your answer as a sequence of numbers in ascending order.
B-2 Match a fat feature with an example of a fat that matches that feature. Give your answer as a sequence of numbers corresponding to letters in alphabetical order:
CHARACTERISTIC:
A) solid fat of vegetable origin
B) solid fat of animal origin
C) liquid fat of animal origin
D) liquid fat of vegetable origin
1) Linseed oil
2) Butter
3) Fish oil
4) Palm oil
Hello. Help me please. 1) Specify the number of isomeric carboxylic acids of composition C5H10O2: a) 3 b) 2 c) 4 d)2) When dissolved in water, 1 mol of acetic anhydride forms:
a) 2 moles of ethanol
b) 2 mol of ethanol
c) 2 mol of acetic acid
d) 1 mol of methyl acetate
3) What substances does sodium acetate react with:
a) hydrochloric acid
b) Sodium hydroxide when heated
c) Carbonic acid
4) When interacting ethanol and carbon monoxide (II) under appropriate conditions, it turns out?
a) ethanal
b) propanal
c) propanoic acid
d) methyl acetate
5) What type of reactions can unsaturated carboxylic acids enter into: a) Oxidation
b) Polymerization
c) Connections
d) Esterification
6) What substances does formic acid react with:
a) Copper II chloride
b) Sodium sulfate
c) Potassium bicarbonate
d) ammonia solution of silver oxide I
7) Unlike stearic acid, oleic acid:
a) Liquid at room temperature
b) soluble in water
c) Discolors bromine water
d) Reacts with alkalis
8) What substances react with water:
a) linoleic acid
b) ethanol
c) propanal
d) propane
9) What single reagent can be used to distinguish between solutions of glycerol, propanal, and ethanoic acid:
a) bromine water
b) potassium carbonate
c) copper hydroxide II
d) nitric acid
10) In reactions with what substances with the participation of acetic acid, a hydrostrong group is split off from its molecule:
a) metals
b) alkalis
c) alcohols
d) metal carbonates
Help pliz, solve two problems!: (put 11 points 1) With which of the following substances: sodium hydroxide, bromine water, dimethyl ether -- In contact with 0
- Google+ 0
- OK 0
- Facebook 0