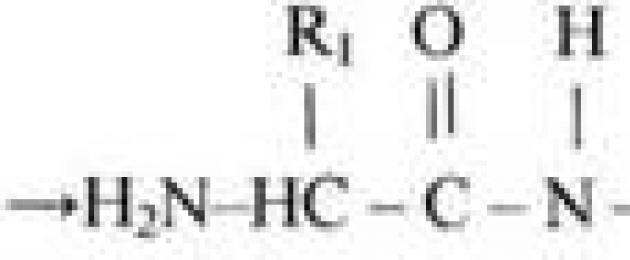"Development of the Earth" - Exhausted, supporting each other, burning our feet on the hot sand, we wandered for five days through the low thickets of thorny eucalyptus bushes. HALL No. 2 1. Based on the proposed pictures, determine the name and show the data natural areas on the map. 2. The sounds we recognize. What does the name mean? HALL No. 1 Practical work: 1. Study the proposed exhibits. 2. Determine: a) What specimens are fossil remains of organisms (fossils) b) What specimens are reconstructed. 3. Formulate a conclusion: Why is it necessary to study the fossil remains of organisms? 4. From the letters proposed, add the name of the science that studies ancient fossils.
"The emergence and development of life" - Hercules and so on. The possibility of a second life on Earth is excluded. Life arose on Earth in an abiogenic way. The world consists of five elements: earth, water, air, fire, and ether. The basis for everything is fire ... Aristotle. The beginnings of the universe are atoms and emptiness. The emergence and initial development of life on Earth.
"Development of the organic world" - Today we are experiencing one of the periods of warming. The supercontinent of Gondwana is spread across the equator. PALEOCENE AGE (Tertiary). Vegetable world As the climate cooled, the forests were replaced by steppes. Duration: FROM 570 TO 500 MILLION Cainozoic era (era of new life). Duration: FROM 65 TO 55 MILLION
"Theory of Life" - Scientific. Let's remember monotheism. Monotheism is one of the directions of creationism. Consider the example of Christianity. BUT still, in religion Ancient egypt many gods remain. Spontaneous origin of life: Democritus began life in silt, Thales - in water, Anaxagoras - in the air. Ancient Egypt.
"Education of Life" - Paleozoic. Star formation. Archaea. Proterozoic.
"Development of Life on Earth" - The project is designed for two weeks. Project on the topic Stages of development of life on Earth. The creative title is "Imperturbable structure in everything, complete harmony in nature" FITyutchev. Developing: promote development information culture and generating interest in research work... Subject: biology. © MOU Lyubimskaya Secondary School, 2010
There are 20 presentations in total
summaries of other presentations“Concepts of the Origin of Life” - Problem. Primary genetic material. The main difficulty of the hypothesis. Problems in modern science... Biochemical evolution. The degree of order. The theory of panspermia. Archbishop Asher. The world of RNA. Interaction. There are many theories about the origin of life. French scientist. Italian biologist. The main postulates of the theory biochemical evolution... The idea of spontaneous generation. Founder of the theory of panspermia.
"The problem of the origin and essence of life" - Natural-historical approach. Oparin. Concept steady state... DNA molecules. The human body weighing 70 kg contains 45.5 kg of oxygen. Chirality property. Creationism. Viruses. Messenger RNA. Anaxagoras. Panspermia concept. The idea of spontaneous generation. Basic provisions. Symposia on the origin of life. Biopolymers. The main merit of Oparin. Biochemical evolution concept.
“How Life on Earth” - The Concept of Biogenesis. Changes in the Earth's atmosphere. L. Pasteur. Van Helmont. Stationary state theory. Spontaneous origin of life. The emergence of life on Earth. The theory of A.I. Oparin. F. Redy. Vitalism. L. Spallanzani. Panspermia. Life in the Earth. Natural origin of life. S. Miller's experience. Theories of the origin of life. Microorganisms. Earth's atmosphere. Creationism. The theory of biochemical evolution.
"Concepts of the origin of life on Earth" - Radiation panspermia. Cell. Evolution theory. The scheme of occurrence. Soviet biochemist. Reverse directional panspermia. The embryos of life. Experiments on the reproduction of amino acids. Chemist Stanley Miller. Plant cell. The theory of panspermia. Creationism. What is life. Vernadsky. Paracelsus. Chemical elements. Living content of the cell. Polypeptides. The theory of spontaneous generation. Formaldehyde. A modern view of the origin of life.
"Theories of the appearance of life" - Organic compounds. Coacervat. Stages of life formation according to Oparin. Organisms are different from non-living ones. Biopoiesis hypothesis. Biogenic method. Van Helmont. Oparin's theory of biochemical evolution. The hypothesis of the spontaneous origin of life on Earth. Stationary hypothesis. French microbiologist Louis Pasteur. Biochemical evolution hypothesis. Panspermia hypothesis. What is life. Protein properties.
"Oldest organisms on Earth" - Oldest organisms. Brachiopod type. List of temporary subdivisions. In what period we live with you. Similarities. Similarities and differences. Equipment. Modern representatives. Jan Baptist Van Helmont. Evolutionary theory. Representatives of the class of bivalve molluscs. The birth of life. Comb lock. Trilobite class. Class Bivalve Molluscs. Geochronological table. The theory of divine origin.
Origin of lifeOrigin of life
1. Coacervates were the first living organisms on Earth.
2. The theory of abiogenesis assumes the possibility of the origin of the living only from the living.
3 .. Pasteur by his experiments proved the impossibility of spontaneous generation of life.
4. The most essential feature of Oparin's hypothesis is the gradual complication chemical structure and morphological exchange of precursors. Life on the way to living organisms.
5. Coacervates are not able to adsorb the substance from the surrounding solution.
6. Life arose biogenic.
7. Life on Earth appeared about 3.5 million years ago
8. At the present time on the Earth spontaneous generation of living organisms is impossible.
9. Coacervate is liquid bubbles surrounded by protein films.
10. The first living organisms on our planet were aerobic heterotrophs.
Origin of life
1. Coacervates were the first living organisms on Earth.
2. The theory of abiogenesis assumes the possibility of the origin of the living only from the living.
3 .. Pasteur by his experiments proved the impossibility of spontaneous generation of life.
4. The most essential feature of Oparin's hypothesis is the gradual complication of the chemical structure and morphological exchange of predecessors. Life on the way to living organisms.
5. Coaervates are not able to adsorb matter from the surrounding solution.
6. Life arose biogenic.
7. Life on Earth appeared about 3.5 million years ago
8. At the present time on the Earth spontaneous generation of living organisms is impossible.
9. Coacervate is liquid bubbles surrounded by protein films.
10. The first living organisms on our planet were aerobic heterotrophs.
Origin of life
1. Coacervates were the first living organisms on Earth.
2. The theory of abiogenesis assumes the possibility of the origin of the living only from the living.
3 .. Pasteur by his experiments proved the impossibility of spontaneous generation of life.
4. The most essential feature of Oparin's hypothesis is the gradual complication of the chemical structure and morphological exchange of predecessors. Life on the way to living organisms.
5. Coatsnervates are not able to adsorb a substance from the surrounding solution.
6. Life arose biogenic.
7. Life on Earth appeared about 3.5 million years ago
8. At the present time on the Earth spontaneous generation of living organisms is impossible.
9. Coacervate is liquid bubbles surrounded by protein films.
10. The first living organisms on our planet were aerobic heterotrophs.
« Origin and initial stages origin of life "
I. 1.What the theory of abiogenesis claims: a) spontaneous generation life; b) the origin of life; c) the possibility of the origin of the living from the non-living; d) development of inanimate matter.
2. What is the essence of Richter's theory: a) the emergence of life from a gas-dust cloud; b) life on Earth arose from inorganic substances;
c) life was brought in from other planets;
d) life arose from non-living substances
3. What was the nature of the ideas of ancient people about the origin of life: a) chaotic; b) spontaneous materialistic; c) methodical;
d) scientific
4. What does the term "spectroscopy" mean: a) a point on a straight line; b) the most important point of contact between astronomy and chemistry; c) spectral analysis;
d) studying the spectrum
5. Protostars are: a) clouds; b) clouds; c) stars; d) planets
6. What chemical element is part of the stellar and solar matter: a) barium; b) chlorine; c) hydrogen; d) oxygen
7. What is the great merit of A. Oparin's theory in: a) the creation of the coacervate theory; b) the concentration of chemicals; c) in the difference between speed and time; d) obtaining organic substances
8. Who obtained the amino acids: a) Haeckel and Müller;
b) Aristotle and Empedocles; c) Yuri and Miller;
d) Pasteur and Pfluger
9. Coacervates are: a) molecules surrounded by a dense shell;
b) molecules surrounded by a water shell, which combine into multimolecular complexes; c) macromolecules that decompose into monomers; d) molecules that burn in atmospheric oxygen
10. Organic substances that do not dissolve in water are called:
a) hydrophobic; b) hydration; c) hydrogenated; d) hydrophilic
11. The essence of the process of photosynthesis is: a) metabolism;
b) in the transport of substances; c) the synthesis of organic substances; d) in the presence of vacuoles
12.Important substance required for the process of photosynthesis:
a) the presence of leukoplasts; b) the presence of chloroplasts; c) the presence of a karyotype;
d) the presence of a plasma membrane
13. What belongs to autotrophic organisms: a) bacteria; b) plants;
c) mushrooms; d) animals
14. Bacteria living in an oxygen-free environment are called: a) anaerobic;
b) protobionts; c) aerobic; d) autotrophic
15. Phagocytosis is a process: a) absorption of liquid products;
b) selection carbon dioxide; c) absorption of solid particles;
d) metabolism
II. Choose the correct judgments from the proposed ones.
The theory of abiogenesis assumes the possibility of the origin of living things only from living things.
L. Pasteur by his experiments proved the possibility of spontaneous generation of life.
The most essential feature of A.I. Oparin's hypothesis is the gradual complication of the chemical structure and morphological metabolism of the precursors of life on the way to living organisms.
The lowest and most ancient level of life organization is the cellular level of life.
Coacervates are not able to adsorb substances from the surrounding solution.
Organism - a complex system capable of self-regulation.
Coacervates are the first ancient living creatures.
Life arose biogenic.
The living is characterized by the ability to historical development and changing from simple to complex.
L. Pasteur by his experiments proved the impossibility of spontaneous origin of life.
III. Establish correspondence.
A - abiogenesis. B - Oparin's hypothesis. B - coacervates. D is an open system. D - heterotrophs. E - autotrophs. F - biogeochemistry. Z - life. And - death. K is a planet.
Heavenly body.
The emergence of living bodies from substances of inorganic nature.
The mode of existence of protein bodies, an essential point of which is a constant exchange of substances with their environment.
The formation of organic substances from inorganic ones took place in the waters of the primary ocean more than 3.5 billion years ago, while in an oxygen-free environment the atmosphere was saturated with aldehydes, alcohol, amino acids.
Bubbles of liquid surrounded by protein films.
Living body.
Organisms that synthesize organic substances necessary for life from inorganic ones.
A science that studies the chemical composition of living matter and geochemical processes constantly occurring in the biosphere with the participation of living organisms.
Organisms that use ready-made organic substances for their nutrition.
The death of an individual in a population.
Answers: 1c, 2c, 3b, 4b, 5a, 6c, 7a, 8c, 9b, 10a, 11c, 12b, 13b, 14c, 15c
Answers: 3,6,10
Answers: 1-k, 2-a, 3-z, 4-b, 5-c, 6-d, 7-th, 8-f, 9-d, 10-i.
FEDERAL EDUCATION AGENCY
State educational institution higher
Secondary technical faculty
Department of Mathematical and Natural Science Disciplines
BIOLOGY
Lecture notes
for 1st year students
all forms of education
Kemerovo 2010
Compiled by:
Teacher,
Reviewed and approved at the meeting
Department of Mathematics and Natural Sciences
secondary technical faculty
I know general biology the main aspects of the existence and functioning of living systems are considered, in conjunction with environment... And also, the basics of selection of living organisms and genetic engineering. Much attention is paid to the disclosure of the theory of evolution.
© Kem TIPP, 2010
FOREWORD
Our time is characterized by an extremely increased interdependence of people. A person's life, his health, his working and living conditions almost entirely depend on the correctness of decisions made by many other people. In turn, the activity of an individual has the same effect on the fate of many others. That is why it is very important that the science of life becomes an integral part of the worldview of every person, regardless of his specialty. A builder, technologist, ameliorator needs knowledge of biology in the same way as a doctor or an agronomist, because only in this case they will represent the consequences of their production activities for nature and man.
The purpose of this course of lectures is to give an idea of the structure of living matter, its most general laws, to acquaint with the diversity of life and the history of its development on Earth. In accordance with this, special attention is paid to the analysis of the relationship between organisms and the conditions for the stability of ecosystems. The course provides examples that characterize the subordination of a person to all known biological laws.
SECTION 1 ORIGIN AND INITIAL STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT OF LIFE ON EARTH
Topic 1.1 Diversity of the living world. The main
properties of living
Terminology
1. Inorganic compounds- elements and simple and complex substances formed by them, found in large quantities outside living organisms.
2. Organic compounds- compounds of carbon with other elements, found mainly in living organisms.
3. Biopolymers- high molecular weight organic compounds, the monomers of which are simple organic molecules.
4.Cell- structural and functional unit, as well as the unit of development of all living organisms.
5. Textile- a set of cells similar in structure, associated with the implementation of common functions.
6. Organ- a set of spatially isolated tissues, specialized in the performance of certain functions.
7. Biological system – biological objects of varying degrees of complexity, having several levels of organization. Possesses the properties of the whole.
Biology Is the science of life. Biology studies the structure, manifestation of life, the habitat of all living organisms on the planet. Life on the planet is represented by an extraordinary variety of forms, many types of living beings. Scientists are constantly finding and describing new species, both existing and extinct in bygone eras.
One of the main tasks of biology is the disclosure of the general properties of living organisms and the explanation of the reasons for their diversity, the identification of connections between the structure and living conditions.
Of great importance in science are the issues of the origin and laws of the development of life on Earth - evolutionary teaching... Understanding these laws is the foundation of the scientific worldview.
According to the subject of study, biology is divided into separate sciences:
Botany;
Zoology;
Anatomy;
The medicine;
Ecology, etc.
Each of these sciences has its own subdivisions and, thanks to the accumulated knowledge, is increasingly specialized.
In accordance with the level of organization of living matter, scientific disciplines: molecular biology, cytology - the study of the cell, histology - the study of tissues, etc.
Biology uses a variety of research methods:
1. historical;
2. descriptive;
3. instrumental.
In various fields of biology, the importance of borderline disciplines is growing more and more: biophysics, biochemistry, bionics.
The emergence of life and the functioning of living organisms are due to natural laws. Knowledge of them allows you to draw up an accurate picture of the world and use it for practical purposes.
Recent advances in biology have led to the emergence of new directions in science, which have become independent sections in the complex. (Genetic Engineering). Practical use achievements of modern biology, currently allows you to get new biological substances - food, drugs, materials. The exceptional ability of nature to heal itself has created the illusion of its invulnerability, the infinity of its resources. But this is not the case. Therefore, all human activities should be based on the principles of the organization of the biosphere.
The importance of biology to humans is enormous. General biological patterns are used in solving a variety of issues in many industries National economy... In agriculture, great strides have been made in developing new varieties cultivated plants, breeds of domestic animals, strains of microorganisms. Further practical significance biology will increase even more. This is due to the rapid growth of the world's population, with an increasing urban population. In such a situation, the intensification of agricultural production is important. Scientifically based use of natural resources will play an important role in this.
The first living things appeared on our planet 3 billion years ago. From these early forms, countless species of living organisms arose, which appeared, flourished for a certain time, and then died out. Modern living organisms have evolved from pre-existing forms, forming the four kingdoms of nature:
More than 1.5 million animal species;
350 thousand plant species;
A significant number of mushroom species;
Many organisms are prokaryotes.
The world of living beings, including humans, is presented biological systems different structural organization... All living organisms are made up of cells. A cell can be a separate organism and part of a multicellular plant or animal. It can be simple or complex. Any cell is a whole organism capable of performing all functions to ensure life. The cells that make up a multicellular organism are specialized - they perform one function and are not able to exist outside the organism. In higher organisms, the interconnection and interdependence of cells leads to the creation of a new quality that is not equal to a simple sum. Their combination in the process of evolution forms an integral organism with certain properties inherent only to it.
Organizational levels of living matter
Wildlife is a complex system.
There are several levels of organization of the living:
1. Molecular(0.1 - 1 mm.) 10m.
The most important vital processes of the organism begin from this level. Any system, no matter how complex it is, is carried out at the level of interaction of biological macromolecules - proteins, polysaccharides, DNA.
2. Cellular(10nm - 1um) 1m.
Cell- the smallest structural unit of all living things. There are no non-cellular life forms. Viruses are an exception since they live only in the cell.
3. Fabric(10μm - 100μm) 1m.
Textile is a collection of cells similar in structure, united by the performance of a common function.
4.Organ(100μm - 1mm) 1m.
Organ Is a structural and functional association of several types of tissues.
5. Organic(1mm - 1dm) 1m.
Organism Is the simplest unicellular or multicellular system capable of independent existence. It is formed by a collection of tissues and organs.
6. Population-specific.
The totality of organisms of one species, united by a common habitat, creates a population in which elementary evolutionary transformations take place.
7. Biogeocenotic.
Biogeocenosis is a set of organisms of different types and different complexity of organization with all environmental factors.
8. Biosphere.
This highest level organization of life. It includes - living matter, inert matter and bio-inert matter.
The biomass of the planet is 2.5 · 1012 tons. Of these, 99% of the mass of land organisms is represented by green plants. At the biosphere level, the circulation of substances and the transformation of energy occur, associated with the vital activity of all living organisms on the planet.
Living systems criteria
It is a system of assessments that distinguish living systems from objects. inanimate nature.
1. Features of the chemical composition. The composition of living organisms includes the same chemical elements as objects of inanimate nature. However, their ratio is not the same. Elements of inanimate nature are presented: O2, Si, Fe, Mg, Al, S, MeO, MeS, MeCO3, etc. In living organisms, 98% of the composition is O2, C, N2, H2. They are part of complex organic molecules: proteins, DNA, carbohydrates, fats.
2. Metabolism. All living organisms are capable of metabolism with the environment. The most important processes are fusion and decay. Living organisms absorb various substances from the environment, they are processed. Part goes to the construction of the body, part - to replenish energy costs. This is assimilation or plastic exchange. This is dissimilation or energy exchange, when organic compounds break down into simple ones and energy is released. Metabolism provides homeostasis of the body - this is the constancy of its structure and functions.
3. Unified principle of structural organization. All organisms at any level of complexity and size are composed of cells.
4. Reproduction. At the organismic level, reproduction is manifested in the form of reproduction of individuals. The offspring are similar to the parents. Self-reproduction is based on the matrix synthesis reaction during DNA self-doubling.
5. Heredity... This is the ability of organisms to transmit their characteristics, properties, abilities from generation to generation. Heredity ensures material continuity across generations.
6. Growth and development. The ability to develop is a universal property of matter. Development is understood as an irreversible directed change in natural objects. As a result, a new, qualitative state of the object arises, its composition and structure change.
A) individual - ontogenesis.
B) historical - phylogeny.
7. Irritability. This is the property of living organisms to selectively respond to external influences. Multicellular organisms respond to irritation by means of a reflex. Organisms without nervous system they react with tropisms - the direction of growth, movement (heliotropism - movement towards the sun).
8. Discreteness. This is a property of living matter. It goes from simple to complex. Discreteness of the structure of an organism is the basis of its structural order.
9. Autoregulation... This is the ability of living organisms in a changing environment to maintain the constancy of chemical composition and the intensity of physiological processes. This activity is regulated by the function of special systems.
10. Volatility. Living bodies are energetically open systems. Metabolic processes are carried out in them through the membranes (membranes, skin). They maintain the consistency of the composition and the unity of the system. Living organisms exist with a constant supply of matter and energy from the outside.
A life- it is an active maintenance and self-reproduction of a specific structure, going with the expenditure of energy received from the outside.
Control questions
1. The essence of the term "Biology".
2. Division of biology by subject of study.
3. Division of biology according to the level of organization.
4. The importance of biology for humans.
5. The diversity of the living world.
6. Biological systems.
7. Levels of organization of the living.
8. Criteria for living systems.
Topic 1.2 The emergence of life on Earth
Terminology
1. Nebula- an accumulation of gaseous and dusty matter in the universe, which is large.
2. Galaxy- the star and the planets surrounding it.
3. star system- a system of stars with the planets surrounding them, developing from one nebula.
4. Planet – heavenly body, moving in a close to circular orbit around the star, glowing with reflected light.
5. Abiogenic synthesis- the formation of organic molecules from inorganic ones outside living organisms.
6. Energy- general quantitative measure of the momentum of matter.
7. Solution- homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances distributed in a solvent.
8. Coacervation - separation of the IUD solution into phases with a higher and lower concentration of molecules.
9. Coacervate- bubbles of liquid surrounded by protein films.
10. Adsorption- absorption of a substance from a liquid medium by a solid surface.
The question of the origin of life on Earth, as well as, probably, on other planets of other stellar systems, worried man from the time he began to realize himself as a man, began to know himself and the world around him. The first attempts at a theoretical solution to the issue date back to ancient times and bear the imprints of those eras and views. Since ancient times, there are two points of view on this issue: one asserts the possibility of the origin of the living from the nonliving - this is the theory of abiogenesis, the other - the theory of biogenesis - denies the spontaneous origin of life. Modern views only make it possible to put this dispute on a scientific basis and thereby substantiate the correctness of the theory of abiogenesis.
Representations of ancient and medieval philosophers
The general level of knowledge in ancient world was short, the views were fantastic. Ignorance of the methods of reproduction of organisms served as the reason for what was believed possible occurrence living beings from dead remains, or inorganic substances. These views were supported by the church. The discovery of the microscope expanded the understanding of the structure of organisms, the theory of the origin of the living from the non-living was rejected. The experiences of the Italian Redi ( mid XVII c.) it was proved that all living things come from living things. However, the theory of spontaneous generation of the living from the non-living existed for a long time in the ears of scientists. The experiments of the Frenchman L. Pasteur finally dispelled this theory. On the basis of Pasteur's work, methods of sterilization and preservation were developed. This happened in 1870.
Later, this issue was transferred to the cell, and microorganisms were no longer considered. Simultaneously with the works of Pasteur, the theory of the eternity of life arose. According to Richter's theory, life was brought to Earth from other planets in 1865. This theory does not reveal the essence of the origin of life, it only tries to explain its appearance.
A special place in the solution of the problem belongs to materialistic theories. The key issue here is the difference between living and non-living. Scientists take the formation of protein compounds as the basis for the origin of living things. According to the theory of the Englishman Ellen in 1899. the first appearance of nitrogenous compounds on Earth coincided with the period when water vapor condensed into water and covered the planet's surface. The water was saturated with salts, which are essential for the formation and activity of protein. In this hot solution, in the presence of ultraviolet radiation, electrical discharges, and a large amount of carbon dioxide, the birth of living things began, which subsequently went through a long evolutionary path.
Investigating the question of the origin of living things at the same time, one should understand the processes taking place during the formation of the planet. The answer to these questions is given by astronomy and chemistry. The main method of space exploration is spectroscopy. Analysis of the light emitted by stars provides a wealth of information about their chemical composition. Since the end of the 19th century. was registered 2 million. spectra of 15 thousand stars and the Sun. Conclusion - the same chemical elements exist everywhere and the same physical laws are fulfilled. Formation of the planet.
The most common element is hydrogen (H-H, H-He). In a universe formed from hydrogen, stars are formed as primary matter. Basic nuclear reaction is the fusion of hydrogen nuclei and the formation of a helium atom and the release of energy. This energy drives the universe. According to the law of conservation of masses, the energy released during the formation is converted into radiation energy. Further interaction of elements leads to the formation of others chemical elements... These reactions are expressed in the formation of more complex molecules and their aggregates - dust particles. They form accumulations of gas and dust matter in space. For example, the giant nebula in the constellation Orion. Its diameter is 15 light years, and the amount of dust is enough to form 100 thousand stars the size of the Sun. The Milky Way Nebula is 100,000 light-years across. The Orion Nebula is the closest to us, at a distance of 1,500 light years. The Earth and other planets were formed from a gas and dust cloud 4.5 billion years ago solar system... Despite the common origin of the planets, life appeared only on Earth and reached exceptional diversity. For the emergence of life on Earth, cosmic and planetary conditions were necessary. First, it is the optimal size of the planet. Secondly, movement in a circular orbit provides constant heat. Thirdly, the constant radiation of the luminary. All these conditions were satisfied by the Earth, on which, about 4.5 billion years ago, conditions were created for a higher level of development of matter and its evolution towards the origin of life.
Modern ideas about the origin of life. All modern ideas about the origin of life on Earth are based on the recognition of the abiogenic, i.e. nonbiological, origin of organic substances from inorganic molecules. This is the opinion of a Russian scientist (1924).
Chemical evolution
In the early stages, the Earth had a very high fever... As it cooled down, heavy elements moved to its center, while the light ones remained on the surface. The metals were oxidized and there was no free oxygen in the atmosphere. It consisted of H2, CH4, NH3, HCN and was of a reductive nature. This served as a prerequisite for the emergence of organic substances in a non-biological way. Until the beginning of the 20th century, it was believed that they can only occur in the body. In this regard, they were called organic, and substances - minerals, inorganic. In 1953. it was proved that by passing a current through a mixture of gases H2, CH4, NH3, HCN in the absence of oxygen, a mixture of amino acids was obtained. Subsequently, many organic compounds were obtained by the abiogenic method. All of them were subsequently discovered in space.
More than 4 billion years ago, the Miller flask was the entire globe. Volcanoes erupted, lava flowed, steam swirled, lightning flashed. As the planet cooled, water vapor condensed and rained down on the planet over millions of years. A primary ocean was formed, hot and saturated with salts, in addition, the resulting sugars, amino acids, and organic acids got there. As the climate softened, the formation of more complex compounds became possible, resulting in the appearance of primary biopolymers - polynucleotides and polypiptides.
The primary ocean contained various organic and inorganic molecules in a soluble form. Their concentration constantly increased and gradually the waters became a "broth" of nutritious organic compounds. Each molecule has a certain structural organization: some are dissociated, some have hydration shells. Organic molecules have great molecular weight and a complex structure. Molecules surrounded by an aqueous shell combine to form high molecular weight complexes - coacervates. In the primary ocean, coacervate droplets absorbed other substances, either disintegrated or enlarged. As a result, the droplets became more complex and adapted to external conditions. Among the coacervates, the selection of the most resistant forms began. Differences appeared between the chemical composition of the internal and external environment. As a result of chemical evolution, those forms have survived that, when decaying into daughter ones, did not lose their structural features. This is the ability to reproduce itself. In the process of evolution, the connection of nucleic acids and protein molecules led to the emergence genetic code... This nucleotide sequence served as the information for the amino acid sequence in the protein molecule. (Reproduction of their own kind). Gradually, the layers of lipids around the coacervates were transformed into an outer membrane. This predetermined the paths of further evolution. The formation of primary cellular organisms marked the beginning of biological evolution.
The emergence of prokaryotes
The selection of coacervates lasted for about 750 Ma. As a result, nuclear-free - prokaryotes appeared. By the way they were solved, they were heterotrophs - they used the organic matter of the primary ocean. In the absence of atmospheric oxygen, they had anaerobic metabolism. It is ineffective. Gradually, the supply of food in the ocean was depleted. Competition for food began.
Organisms capable of using solar energy for the synthesis of organic matter turned out to be in a more advantageous position. This is how photosynthesis arose. This led to the emergence of a new power source. Then photosynthetic organisms learned to use water as a source of hydrogen. The assimilation of carbon dioxide in them was accompanied by the release of oxygen and the incorporation of carbon into organic compounds. (Today, ocean surface prokaryotes produce up to 78% renewable oxygen.)
The transition from a primary atmosphere to an oxygen environment is very significant event... V upper layers an ozone screen is formed, a more beneficial oxygen type of metabolism appears. New forms of life began to emerge on Earth, with greater use of the environment.
The emergence of eukaryotes
Eukaryotes are the result of the symbiosis of various prokaryotes. This is how the ancestors of the primitive living flagellate protozoa arose. The symbiosis of flagellates with photosynthesizing algae or plants.
The possibilities of unicellular organisms in the development of their habitat were limited. Multicellular organisms appeared 2.6 billion years ago. The basis of modern ideas about the origin is explained by the theory of phagocytella. Multicellular organisms evolved from colonial flagellates. They still exist. These colonies have become the simplest, but complete organism.
Thus, the emergence of life on Earth is associated with a long process of chemical evolution. The formation of the membrane - the shell contributed to the beginning of biological evolution. Both the simplest and the complex ones have a cell in the basis of their structural organization.
Control questions
1. The history of ideas about the origin of life.
2. Works by L. Pasteur.
3. The theory of eternity of life.
4. Formation of inorganic substances and the formation of the planet.
5. Theory.
6. Biological evolution.
7. The emergence of the first multicellular organisms.
Chapter2 Cytology - THE TEACHING ABOUT THE CELL
Topic 2.1 Chemical organization of the cell. Macro - and trace elements
Terminology
1. Bioelements- chemical elements that are the basis of organic molecules.
2.Macronutrients- chemical elements that make up organic molecules in an amount exceeding 1%.
3. Trace elements- chemical elements included in the composition of organic molecules in an amount not exceeding 0.001%.
4. Homeostasis- a state of dynamic equilibrium natural system supported by the activities of regulatory systems.
5. Buffer solutions- a solution of organic or inorganic substances, the pH value of which does not change when small amounts of alkali or acid are added.
The simplest microorganisms are single cells. The body of all multicellular organisms consists of more or fewer cells, which are the blocks that form a living organism. Regardless of whether a cell is an integral system or a part of it, it has a set of features common to all cells.
Chemical organization of cells
The cells contain about 70 elements periodic system found in inanimate nature. This is one of the proofs of the commonality of animate and inanimate nature. However, the ratio of elements, their contribution to the formation of the elements that make up the organism and inanimate, differ sharply.
Depending on the ratio of elements in the composition of the body, there are:
1.macroelements (98% of the cell mass) H2, O2, C, N.
2.trace elements (1.5%) S, P, K, Na, Ca, Mg, Mn, Fe, Cl. Each of them performs very important functions in the cell.
3.other (0.5%) B, Zn, Cu, I2, F2CO, Se.
All these elements are involved in the construction of the organism either in the form of ions, or in the composition of certain compounds - molecules of organic and inorganic compounds.
Inorganic substances in the cell
These include water and mineral salts.
Water- the most widespread inorganic compound in living organisms. Its amount ranges from 10% in the enamel of the teeth to 90% in the cells of the embryos. It depends on age, time of day, time of year.
Water molecules are represented by dipoles: depending on the temperature, the molecules can be free or combine into groups with the presence of hydrogen bonds. The dipole character is responsible for the high chemical activity of the water. Water plays the role of a medium in the cell, it brings in and carries away nutrients. Water undergoes numerous hydrolysis reactions. With good thermal conductivity, water regulates the temperature in the cage.
Mineral salts - it most of inorganic compounds. They are in the form of ions or undissociated molecules. K +, Na +, Ca + 2 are of great importance. They provide a constant water content, solution medium. Buffering of the medium ensures the constancy of all internal processes in the cell.
Organic matter in the cell
They make up 20-30% of the cell mass. These include biopolymers - proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, fats, ATP, etc.
Different types of cells contain different amounts of organic compounds. Complex carbohydrates predominate in plant cells, proteins and fats in animals. Nevertheless, each group of organic substances in any type of cells performs functions: providing energy, being a building material, carrying information, etc.
Proteins. Among organic substances of the cell, proteins occupy the first place in terms of quantity and importance. In animals, they account for 50% of the dry mass of the cell.
The human body contains many types of protein molecules that differ from each other and from proteins of other organisms.
Peptide bond:
When combined, the molecules form: a dipeptide, a tripeptide, or a polypeptide. This is a compound of 20 or more amino acids. The order of transformation of amino acids in a molecule is very diverse. This allows the existence of variants that differ in the requirement and properties of the protein molecules.
The sequence of amino acids in a molecule is called a structure.
Primary is linear.
Secondary - spiral.
Tertiary - globules.
Quaternary - the union of globules (hemoglobin).
Loss of structural organization by a molecule is called denaturation. It is caused by changes in temperature, pH, radiation. With a slight impact, the molecule can restore its properties. It is used medicinally (antibiotics).
The functions of proteins in the cell are varied. The most important is construction. Proteins are involved in the education of all cell membranes in organelles. The catalytic function is extremely important - all enzymes are proteins. The motor function is provided by contractile proteins. Transport - consists in attaching chemical elements and transferring them to tissues. The protective function is provided by special proteins - antibodies formed in leukocytes. Proteins serve as a source of energy - when complete splitting 1 g of protein is released 11.6 kJ.
Carbohydrates. These are compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Presented by sugars. The cell contains up to 5%. The richest - plant cells- up to 90% of the mass (potatoes, rice). They are divided into simple and complex. Simple - monosaccharides (glucose) С6Н12О6, grape sugar, fructose. Disachara - (sucrose) C] 2H22O11 beet and cane sugar. Polysaccharides (cellulose, starch) (C6H10O5) n.
Carbohydrates perform mainly construction and energy functions. When 1 g of carbohydrate is oxidized, 17.6 kJ is released. Starch and glycogen are the energy store of the cell.
Lipids. These are fats and fat-like substances in the cell. They are esters of glycerol and high molecular weight saturated and unsaturated acids. They can be solid and liquid - oils. Plants contain in seeds, from 5-15% of dry matter.
The main function is energy - when 1 g of fat is broken down, 38.9 kJ is released. Fats are stores of nutrients. Fats have a building function and are a good heat insulator.
Nucleic acids. These are complex organic compounds. Consist of C, H2, O2, N2, P. Contained in the nuclei and cytoplasm.
 |
a) DNA is a biological polynucleotide consisting of two chains of nucleotides. Nucleotides - consist of 4 nitrogenous bases: 2 purines - Adenine and Valine, 2 pyrimidines of Cytosine and Guanine, as well as sugar - deoxyribose and a phosphoric acid residue.
In each strand, nucleotides are linked by covalent bonds. The chains of nucleotides form spirals. A DNA spiral packed with proteins forms a structure - a chromosome.
b) RNA is a polymer, the monomers of which are nucleotides close to DNA, nitrogenous bases - A, G, C. Instead of thymine, there is Uration. RNA carbohydrate is ribose, there is a phosphoric acid residue.

Double-stranded RNA carriers genetic information... Single-stranded - carry information about the sequence of amino acids in a protein. There are several single-stranded RNAs:
Ribosomal - 3-5 thousand nucleotides;
Informational - nucleotides;
Transport - 76-85 nucleotides.
Protein synthesis is carried out on ribosomes with the participation of all types of RNA.
Control questions
1. Is a cell an organism or a part of it?
2. Elementary composition of cells.
3. Water and minerals.
4. Organic matter of the cell.
6. Carbohydrates, fats.
Topic 2.2 Structure and function of the cell
Terminology
1. Biological membrane- a bimolecular layer of phospholipids with various protein molecules immersed in it from different sides.
2. Organelles- strictly specialized structures constantly present in the cytoplasm.
3. Cytoskeleton- a system of microtubules and protein fibers, which maintains the shape of cells and the vastness of structures in the cytoplasm.
4. Mitochondria- energy stations of the cell, on the membranes of which the enzymes of energy metabolism are arranged in an orderly manner.
5. Plastids- organelles in which photosynthesis takes place.
6. Inclusions- structures that are not permanently present in the cytoplasm, which are the products of the vital activity of cells and play the role of a reserve of nutrients.
Biochemical transformations are inextricably linked with various structures of a living cell, which are responsible for the performance of a particular function. Such structures are called organelles, since, like the organs of the whole organism, they perform a specific function. According to the level of organization (degree of complexity), all cells are divided into non-nuclear - prokaryotes and nuclear - eukaryotes. Bacteria and blue-green algae are nuclear-free. To eukaryotes - cells of fungi, animals and plants.
Thus, in modern science, two levels of cellular organization are distinguished: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotes retain the features of the deepest antiquity: they are very simply arranged. On this basis, they are distinguished into an independent kingdom - scraps.
Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus limited by a membrane, as well as complex "power stations" - mitochondria. In other words, all cells nuclear organisms highly organized, adapted to the consumption of oxygen and therefore can produce large amounts of energy.
The structure of prokaryotes
Bacteria are typical prokaryotes. They live everywhere: in water, soil, food. The list of habitats shows what high degree adaptability is possessed by prokaryotes, despite the simplicity of their structure. Bacteria are primitive life forms and it can be assumed that they originated in the earliest stages of the development of life on Earth. The bacteria originally lived in the seas. Modern microorganisms originated from them. A person became acquainted with the world of microbes after making a lens with high magnification.
- In contact with 0
- Google+ 0
- OK 0
- Facebook 0